Android HttpURLConnection网络访问方法及实现疑问
- 行业动态
- 2025-03-04
- 4
java,// 创建URL对象,URL url = new URL("http://example.com");,// 打开连接,HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();,// 设置请求方法,connection.setRequestMethod("GET");,// 获取响应码,int responseCode = connection.getResponseCode();,// 读取响应内容,InputStream inputStream = connection.getInputStream();,BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));,String line;,StringBuilder response = new StringBuilder();,while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {, response.append(line);,},// 关闭流和连接,reader.close();,connection.disconnect();,“
以下是关于Android用HttpURLConnection访问网络的方法的详细回答:
一、添加网络权限
1、在AndroidManifest.xml中添加权限
INTERNET权限:允许应用访问互联网。
ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE权限:允许应用访问网络状态信息。
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.ACCESS_NETWORK_STATE"/>
2、设置应用支持明文流量
在Android 9.0(API级别28)及更高版本中,默认情况下不允许应用使用明文流量(HTTP),为了允许应用使用明文HTTP流量,需要在AndroidManifest.xml的application节点添加如下属性:
<application
...
android:usesCleartextTraffic="true">
...
</application> 二、获取HttpURLConnection实例
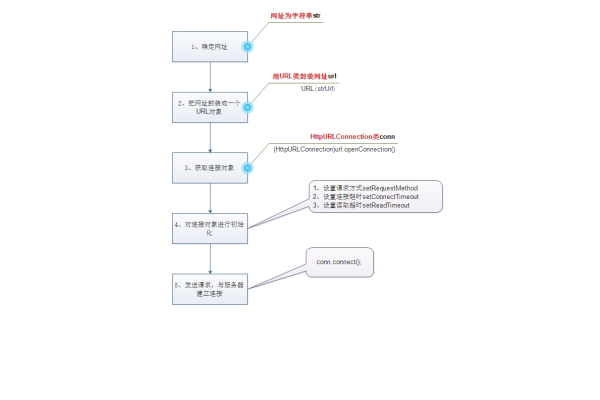
1、创建URL对象
使用要访问的网络地址创建一个URL对象,要访问百度网站,可以这样写:
URL url = new URL("https://www.baidu.com"); 2、打开连接
调用URL对象的openConnection()方法来获取HttpURLConnection实例:
HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
三、设置请求属性
1、设置请求方式
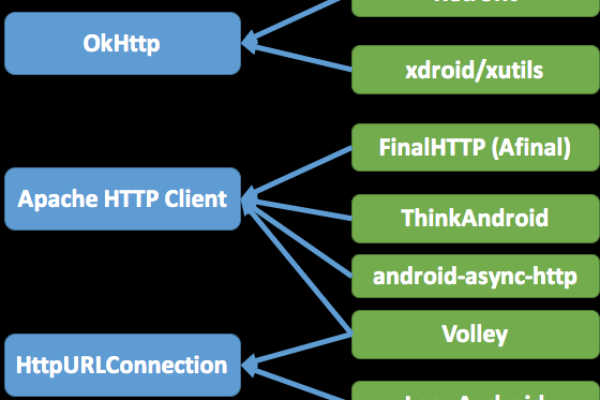
常见的请求方式有GET和POST,可以通过setRequestMethod()方法设置请求方式:
connection.setRequestMethod("GET"); // 或者 "POST" 2、设置超时时间
可以设置连接超时时间和读取超时时间,单位为毫秒:
connection.setConnectTimeout(8000); // 连接超时时间为8秒
connection.setReadTimeout(8000); // 读取超时时间为8秒 3、设置请求头
如果需要设置请求头,可以使用setRequestProperty()方法:
connection.setRequestProperty("key", "value"); 四、发送请求并获取响应
1、对于GET请求
直接调用getInputStream()方法获取服务器返回的输入流:
InputStream inputStream = connection.getInputStream();
2、对于POST请求

需要先设置DoOutput为true,然后通过输出流写入数据,再调用getInputStream()方法获取响应:
connection.setDoOutput(true);
OutputStream outputStream = connection.getOutputStream();
DataOutputStream dataOutputStream = new DataOutputStream(outputStream);
dataOutputStream.writeBytes("username=admin&password=888888");
dataOutputStream.close();
InputStream inputStream = connection.getInputStream(); 3、读取响应数据
使用BufferedReader对输入流进行读取,并将数据保存到字符串中:
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(inputStream));
StringBuilder response = new StringBuilder();
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null) {
response.append(line);
}
reader.close(); 五、关闭连接
1、关闭输入流
读取完数据后,需要关闭输入流:
if (reader != null) {
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} 2、断开连接
断开与服务器的连接:
if (connection != null) {
connection.disconnect();
} 六、在子线程中执行网络请求
1、启动新线程
由于网络请求可能耗时较长,应该在子线程中执行:
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 在这里执行网络请求代码
}
}).start(); 2、切换到主线程更新UI
如果需要在网络请求完成后更新UI,可以使用runOnUiThread()方法切换到主线程:
runOnUiThread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 在这里更新UI元素
}
}); 相关问题与解答
1、问题:为什么HTTP访问不能在主线程进行?
答案:在Android中,从API level 11(Android 3.0 Honeycomb)开始,Google规定不能在主线程中进行网络操作,否则会抛出NetworkOnMainThreadException异常,这是因为网络操作可能会阻塞主线程,导致界面卡顿甚至ANR(Application Not Responding)错误,所有的网络请求都应该放在子线程中执行。
2、问题:如何判断HttpURLConnection是否成功连接到服务器?
答案:可以通过检查HttpURLConnection的响应码来判断是否成功连接到服务器,如果响应码是HTTP_OK(即200),则表示连接成功并且服务器正确响应了请求,可以使用以下代码进行检查:
if (connection.getResponseCode() == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK) {
// 连接成功,处理响应数据
} else {
// 连接失败,处理错误情况
}