如何使用FFmpeg将网络流保存到内存中?
- 行业动态
- 2024-12-28
- 4643
使用ffmpeg将网络流保存到内存,可以使用以下命令: ffmpeg -i -f mp4 pipe:1 > output.mp4。
使用FFmpeg将网络流保存到内存中是一项复杂但非常有用的技能,以下是详细的步骤和相关代码示例,帮助你实现这一目标。
注册所有的组件
FFmpeg需要注册各种组件,包括编解码器、滤镜特效处理库等,这些组件是处理多媒体数据的基础。
av_register_all();
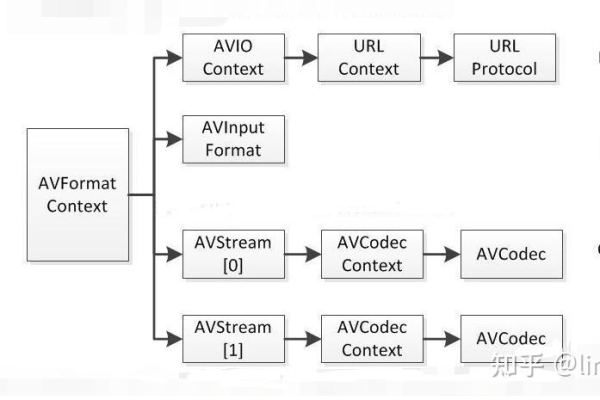
2. 获取视频流的封装信息并查找视频和音频流的位置
在这一步,你需要打开输入的网络流并获取其封装信息,以便找到视频和音频流的位置。
AVFormatContext *inputContext = avformat_alloc_context();
int ret = avformat_open_input(&inputContext, "rtsp://your_stream_url", NULL, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Could not open input stream
");
return ret;
}
ret = avformat_find_stream_info(inputContext, NULL);
if (ret < 0) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Could not find stream information
");
return ret;
}3. 查找视频和音频解码器ID,根据解码器ID打开解码器
找到视频和音频流的解码器ID后,可以根据这些ID打开相应的解码器。
AVCodecParameters *audioParams = inputContext->streams[audioStreamIndex]->codecpar; AVCodecParameters *videoParams = inputContext->streams[videoStreamIndex]->codecpar; AVCodec *audioDecoder = avcodec_find_decoder(audioParams->codec_id); AVCodec *videoDecoder = avcodec_find_decoder(videoParams->codec_id); AVCodecContext *audioCodecContext = avcodec_alloc_context3(audioDecoder); AVCodecContext *videoCodecContext = avcodec_alloc_context3(videoDecoder); avcodec_parameters_to_context(audioCodecContext, audioParams); avcodec_parameters_to_context(videoCodecContext, videoParams);
创建输出流并拷贝流上下文信息
在这一步,你需要创建一个输出流,并将输入流的上下文信息拷贝到输出流中。
AVFormatContext *outputContext = NULL; avio_alloc_context(outputBuffer, outputBufferSize, 1, &outputContext, NULL, writePacket, NULL); outputContext->flags |= AVFMT_FLAG_CUSTOM_IO;
5. 循环读取网络流,解码packet并写入本地
这是最关键的一步,通过循环读取网络流,解码每个packet并将其写入输出流。
while (av_read_frame(inputContext, packet) >= 0) {
// Decode audio and video packets
if (packet->stream_index == audioStreamIndex) {
avcodec_send_packet(audioCodecContext, packet);
AVFrame *frame = av_frame_alloc();
int ret = avcodec_receive_frame(audioCodecContext, frame);
if (ret >= 0) {
// Process the audio frame here
av_frame_free(&frame);
}
} else if (packet->stream_index == videoStreamIndex) {
avcodec_send_packet(videoCodecContext, packet);
AVFrame *frame = av_frame_alloc();
int ret = avcodec_receive_frame(videoCodecContext, frame);
if (ret >= 0) {
// Process the video frame here
av_frame_free(&frame);
}
}
av_packet_unref(packet);
}关闭解码器释放内存
最后一步是关闭解码器并释放所有分配的内存。
avcodec_free_context(&audioCodecContext); avcodec_free_context(&videoCodecContext); avformat_close_input(&inputContext);
表格:关键函数及其作用
| 函数名 | 作用 |
| av_register_all() | 注册所有FFmpeg组件。 |
| avformat_open_input() | 打开输入的网络流。 |
| avformat_find_stream_info() | 获取网络流的封装信息。 |
| avcodec_find_decoder() | 根据解码器ID查找解码器。 |
| avcodec_alloc_context3() | 分配解码器上下文。 |
| avcodec_parameters_to_context() | 将参数转换为解码器上下文。 |
| avio_alloc_context() | 为自定义IO分配上下文。 |
| av_read_frame() | 读取网络流中的帧。 |
| avcodec_send_packet() | 发送包到解码器。 |
| avcodec_receive_frame() | 接收解码后的帧。 |
| avcodec_free_context() | 释放解码器上下文。 |
| avformat_close_input() | 关闭输入流。 |
FAQs
Q1: 如何从内存中读取网络流?
A1: 使用avio_alloc_context()函数来分配一个自定义的IO上下文,然后重写该上下文的read_packet函数以从内存中读取数据。
static int my_read(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size) {
AVIOBufferContext *bufferContext = (AVIOBufferContext *)opaque;
int len = bufferContext->totalSize bufferContext->pos;
if (len > buf_size) len = buf_size;
memcpy(buf, bufferContext->ptr + bufferContext->pos, len);
bufferContext->pos += len;
return len;
}Q2: 如何将解码后的帧写入内存?
A2: 使用avio_alloc_context()函数来分配一个自定义的IO上下文,然后重写该上下文的write_packet函数以将数据写入内存。
static int my_write(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size) {
AVIOBufferContext *bufferContext = (AVIOBufferContext *)opaque;
if (bufferContext->pos + buf_size > bufferContext->totalSize) return -1; // No space left
memcpy(bufferContext->ptr + bufferContext->pos, buf, buf_size);
bufferContext->pos += buf_size;
return buf_size;
}小编有话说:使用FFmpeg将网络流保存到内存中虽然复杂,但通过合理利用FFmpeg提供的API和自定义IO上下文,可以高效地完成这项任务,希望本文能为你提供有价值的参考,让你在处理多媒体数据时更加得心应手。
本站发布或转载的文章及图片均来自网络,其原创性以及文中表达的观点和判断不代表本站,有问题联系侵删!
本文链接:https://www.xixizhuji.com/fuzhu/377314.html