如何在CSDN上实现JavaScript代码高亮显示?
- 行业动态
- 2025-01-24
- 2371
标签中编写代码并指定语言类型,最后调用hljs.highlightAll()`方法初始化高亮显示。
在CSDN上实现代码高亮显示,通常可以通过引入JavaScript库如Highlight.js或Prism.js来完成,以下是使用这两种库的详细步骤及示例:
使用Highlight.js实现代码高亮
1、引入Highlight.js:需要在HTML文件中引入Highlight.js的CSS和JavaScript文件,可以通过CDN方式引入。
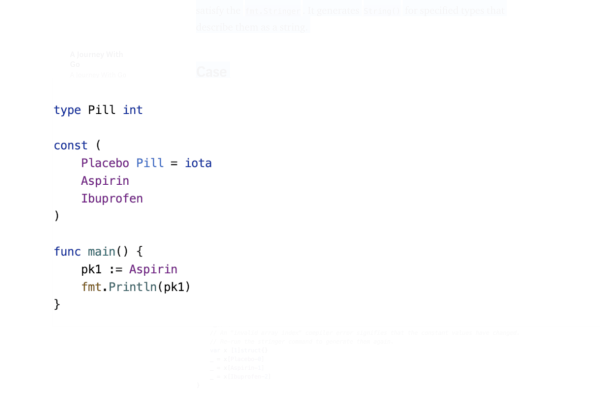
2、编写HTML代码块:在HTML中编写需要高亮的JS代码块,并在<pre><code>标签中添加class="language-javascript"。
3、初始化Highlight.js:在页面加载完成后,调用hljs.highlightAll()方法来初始化Highlight.js。
完整示例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>JS Code Highlight</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="//cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/highlight.js/11.3.1/styles/default.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<pre><code class="language-javascript">
// Example JavaScript code
function sayHello() {
console.log("Hello, World!");
}
sayHello();
</code></pre>
<script src="//cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/highlight.js/11.3.1/highlight.min.js"></script>
<script>
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", (event) => {
hljs.highlightAll();
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
使用Prism.js实现代码高亮
1、引入Prism.js:与Highlight.js类似,需要引入Prism.js的CSS和JavaScript文件,同样可以通过CDN方式引入。
2、编写HTML代码块:在HTML中编写需要高亮的JS代码块,并在<pre><code>标签中添加class="language-javascript"。
3、初始化Prism.js:在页面加载完成后,调用Prism.highlightAll()方法来初始化Prism.js(注意:Prism.js的初始化方法与Highlight.js不同)。
完整示例如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>JS Code Highlight</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/prism/1.23.0/themes/prism.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<pre><code class="language-javascript">
// Example JavaScript code
function sayHello() {
console.log("Hello, World!");
}
sayHello();
</code></pre>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/prism/1.23.0/prism.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/prism/1.23.0/components/prism-javascript.min.js"></script>
<script>
document.addEventListener("DOMContentLoaded", (event) => {
Prism.highlightAll();
});
</script>
</body>
</html>
FAQs
Q1: 如何在CSDN博客中引入Highlight.js或Prism.js来实现代码高亮?
A1: 在CSDN博客中,你可以通过编辑博客文章的HTML源代码,按照上述步骤引入Highlight.js或Prism.js的CSS和JavaScript文件,并编写相应的代码块来实现代码高亮,CSDN博客可能对外部资源的引入有一定的限制或要求,具体请参考CSDN的官方文档或帮助中心。
Q2: Highlight.js和Prism.js哪个更适合用于代码高亮?
A2: Highlight.js和Prism.js都是非常优秀的代码高亮库,选择哪一个取决于你的具体需求和偏好,Highlight.js具有广泛的语言支持和自动检测语言的能力,而Prism.js则提供了更多的定制选项和插件支持,你可以根据项目的实际情况和个人喜好来选择适合的库。
本站发布或转载的文章及图片均来自网络,其原创性以及文中表达的观点和判断不代表本站,有问题联系侵删!
本文链接:http://www.xixizhuji.com/fuzhu/91952.html