C如何实现网络通信功能?
- 行业动态
- 2025-03-04
- 9
System.Net.Sockets命名空间下的
TcpClient或
UdpClient类。对于TCP通信,创建
TcpClient对象,连接到服务器端指定IP和端口,通过
GetStream()获取网络流进行数据读写;对于UDP通信,则使用
UdpClient,通过其
Send和
Receive方法发送与接收数据报。
C# 网络通信详解
在现代软件开发中,网络通信是一个不可或缺的部分,C# 作为一门强大的编程语言,提供了丰富的类库和框架来支持各种类型的网络通信,本文将详细介绍如何在 C# 中进行网络通信,包括基础概念、常用协议以及实际代码示例。
一、网络通信基础概念
网络通信模型
网络通信通常遵循一定的模型,最常见的是 OSI(开放系统互连)七层模型和 TCP/IP 四层模型,在实际应用中,TCP/IP 模型更为广泛使用,它包括以下四层:
应用层:负责为应用程序提供网络服务,如 HTTP、FTP、SMTP 等协议。
传输层:负责端到端的数据传输和可靠性保证,主要包括 TCP(传输控制协议)和 UDP(用户数据报协议)。
网络层:负责数据包的路由和转发,主要协议是 IP(互联网协议)。
链路层:负责物理网络的数据传输,如以太网、Wi-Fi 等。
TCP 与 UDP 的区别
TCP(传输控制协议):
面向连接:在数据传输前需要建立连接,数据传输完成后会断开连接。
可靠传输:通过确认机制、重传机制等保证数据的可靠传输。
有序传输:数据按照发送顺序进行接收和处理。

流量控制和拥塞控制:根据网络状况调整数据传输速度,避免网络拥塞。
UDP(用户数据报协议):
无连接:不需要建立连接即可发送数据,数据传输速度快。
不可靠传输:不保证数据的可靠传输,可能会出现数据丢失、重复或乱序的情况。
无序传输:数据可能不按照发送顺序到达接收方。
无流量控制和拥塞控制:不会根据网络状况调整数据传输速度,可能导致网络拥塞。
二、C# 中的网络通信方式
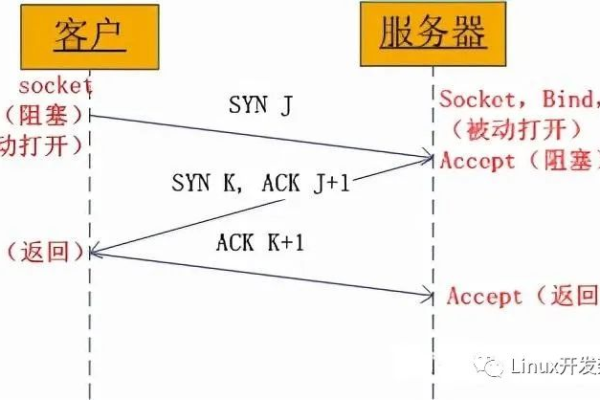
1. 使用 TcpClient 和 TcpListener 进行 TCP 通信
(1)TcpClient 类
TcpClient 类用于创建客户端应用程序,它可以连接到指定的远程主机和端口,并发送和接收数据,以下是一个简单的示例:
using System;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Text;
class TcpClientExample
{
static void Main()
{
// 创建 TcpClient 对象并连接到远程主机和端口
using (TcpClient client = new TcpClient("localhost", 8000))
{
// 获取网络流
using (NetworkStream stream = client.GetStream())
{
// 发送数据到服务器
string dataToSend = "Hello, Server!";
byte[] data = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(dataToSend);
stream.Write(data, 0, data.Length);
// 从服务器接收数据
byte[] buffer = new byte[256];
int bytesRead = stream.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
string receivedData = Encoding.ASCII.GetString(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
Console.WriteLine("Received from server: " + receivedData);
}
}
}
}
在这个示例中,我们首先创建了一个TcpClient 对象,并指定了要连接的远程主机(localhost)和端口号(8000),我们获取了与该连接关联的NetworkStream 对象,并通过它发送和接收数据。
(2)TcpListener 类
TcpListener 类用于创建服务器应用程序,它可以监听指定的本地端口,等待客户端的连接请求,并与客户端进行通信,以下是一个简单的示例:
using System;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Text;
class TcpListenerExample
{
static void Main()
{
// 创建 TcpListener 对象并开始监听指定端口
TcpListener listener = new TcpListener(IPAddress.Any, 8000);
listener.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Server is listening on port 8000...");
while (true)
{
// 等待客户端连接
using (TcpClient client = listener.AcceptTcpClient())
{
Console.WriteLine("Client connected!");
using (NetworkStream stream = client.GetStream())
{
// 从客户端接收数据
byte[] buffer = new byte[256];
int bytesRead = stream.Read(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
string receivedData = Encoding.ASCII.GetString(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
Console.WriteLine("Received from client: " + receivedData);
// 发送数据到客户端
string dataToSend = "Hello, Client!";
byte[] data = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(dataToSend);
stream.Write(data, 0, data.Length);
}
}
}
}
}
在这个示例中,我们首先创建了一个TcpListener 对象,并指定了要监听的本地端口号(8000),我们调用Start 方法开始监听该端口,当有客户端连接时,AcceptTcpClient 方法会返回一个TcpClient 对象,我们可以使用该对象与客户端进行通信。
2. 使用 UdpClient 类进行 UDP 通信
UdpClient 类用于在 UDP 协议上发送和接收无连接的数据报,以下是一个简单的示例:
(1)发送数据
using System;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Text;
class UdpClientSendExample
{
static void Main()
{
// 创建 UdpClient 对象并指定远程主机和端口
using (UdpClient client = new UdpClient("localhost", 8000))
{
// 要发送的数据
string dataToSend = "Hello, UDP Server!";
byte[] data = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(dataToSend);
// 发送数据到服务器
client.Send(data, data.Length);
Console.WriteLine("Message sent to server.");
}
}
}
在这个示例中,我们创建了一个UdpClient 对象,并指定了要发送数据的远程主机(localhost)和端口号(8000),我们将要发送的数据转换为字节数组,并使用Send 方法将其发送到服务器。
(2)接收数据
using System;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Text;
class UdpClientReceiveExample
{
static void Main()
{
// 创建 UdpClient 对象并绑定到本地端口
using (UdpClient client = new UdpClient(8000))
{
Console.WriteLine("Server is listening on port 8000...");
while (true)
{
// 接收数据
IPEndPoint remote = null;
byte[] buffer = client.Receive(ref remote);
string receivedData = Encoding.ASCII.GetString(buffer);
Console.WriteLine("Received from client: " + receivedData);
}
}
}
}
在这个示例中,我们创建了一个UdpClient 对象,并将其绑定到本地端口(8000),我们进入一个无限循环,使用Receive 方法等待接收来自客户端的数据,当接收到数据时,我们将其转换为字符串并输出到控制台。

三、网络通信中的异步编程
在网络通信中,异步编程可以提高应用程序的性能和响应性,C# 提供了多种方式来实现异步编程,例如使用async 和await 关键字、BeginInvoke 和EndInvoke 方法等,以下是使用async 和await 实现异步 TCP 通信的示例:
using System;
using System.Net;
using System.Net.Sockets;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
class AsyncTcpClientExample
{
static async Task Main()
{
// 创建 TcpClient 对象并连接到远程主机和端口
using (TcpClient client = new TcpClient("localhost", 8000))
{
// 获取网络流
using (NetworkStream stream = client.GetStream())
{
// 发送数据到服务器(异步)
string dataToSend = "Hello, Server!";
byte[] data = Encoding.ASCII.GetBytes(dataToSend);
await stream.WriteAsync(data, 0, data.Length);
Console.WriteLine("Data sent to server asynchronously.");
// 从服务器接收数据(异步)
byte[] buffer = new byte[256];
int bytesRead = await stream.ReadAsync(buffer, 0, buffer.Length);
string receivedData = Encoding.ASCII.GetString(buffer, 0, bytesRead);
Console.WriteLine("Received from server: " + receivedData);
}
}
}
}
在这个示例中,我们使用了async 和await 关键字来实现异步的网络通信。WriteAsync 方法用于异步发送数据,ReadAsync 方法用于异步接收数据,这样可以避免阻塞主线程,提高应用程序的性能和响应性。
四、网络通信中的安全问题
在网络通信中,安全是一个非常重要的问题,以下是一些常见的网络安全问题及解决方法:
数据加密
为了防止数据在传输过程中被窃取或改动,可以使用加密技术对数据进行加密,在 C# 中,可以使用System.Security.Cryptography 命名空间下的类来实现数据加密和解密,使用对称加密算法 AES 对数据进行加密:
using System;
using System.IO;
using System.Security.Cryptography;
using System.Text;
class DataEncryptionExample
{
static void Main()
{
// 要加密的数据
string originalData = "Sensitive Information";
byte[] dataToEncrypt = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(originalData);
// 创建加密器(AES)实例
using (Aes aes = Aes.Create())
{
// 生成密钥和向量(IV)
aes.Key = new byte[32]; // AES-256 需要 32 字节的密钥
aes.IV = new byte[16]; // AES 块大小为 16 字节,IV 也为 16 字节
// 创建加密器对象并进行加密操作
using (ICryptoTransform encryptor = aes.CreateEncryptor(aes.Key, aes.IV))
using (MemoryStream ms = new MemoryStream())
using (CryptoStream cs = new CryptoStream(ms, encryptor, CryptoStreamMode.Write))
{
cs.Write(dataToEncrypt, 0, dataToEncrypt.Length);
cs.FlushFinalBlock();
byte[] encryptedData = ms.ToArray();
Console.WriteLine("Data encrypted successfully.");
}
}
}
}
在这个示例中,我们首先将要加密的数据转换为字节数组,然后创建一个Aes 加密器实例,并生成密钥和向量(IV),我们创建一个加密器对象,并将数据写入加密流进行加密操作,我们将加密后的数据输出到控制台,解密过程与加密过程类似,只需使用相应的解密器对象即可。
身份验证和授权
为了确保只有合法的用户能够访问网络资源,需要进行身份验证和授权,在 C# 中,可以使用多种方式实现身份验证和授权,例如使用用户名和密码、数字证书、令牌等,以下是一个简单的基于用户名和密码的身份验证示例:
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Net; using System.Net.Sockets; using System.Text; using System.Threading; using System.Threading.Tasks; using System.Security.Authentication; using System.Security.Principal; using System.Security.Cryptography; using System.Linq; using System.Security.Claims; using Microsoft.IdentityModel.Tokens; using System.IdentityModel.Tokens.Jwt; using System.Text.Json; using System.Text.Json.Serialization; using System.Security.Claims; using System.Globalization; using System.Diagnostics; using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates; using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates; using System.Security.Cryptography; using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates; using System.Security.Cryptography; using System.Security.Cryptography; using System.Security.Cryptography; using System.Security.Cryptography; using System.Security.Cryptography; using System.Security.Cryptography; using System.Security.Cryptography;