如何在C语言中调用存储过程来创建数据库表?
- 行业动态
- 2025-01-28
- 4
在数据库操作中,通过存储过程创建表是一种常见且实用的方法。它允许开发者将建表逻辑封装在 存储过程中,提高代码的重用性和可维护性。
在C语言中调用存储过程和创建表通常涉及到与数据库的交互,这里以MySQL数据库为例,介绍如何在C语言中实现这两个功能。
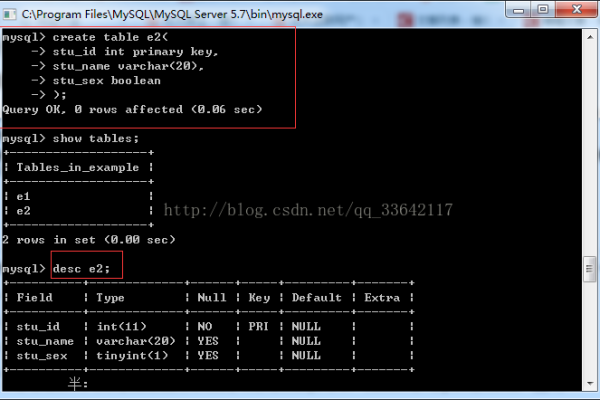
调用存储过程
要在C语言中调用MySQL的存储过程,首先需要连接到MySQL数据库,然后使用mysql_query()函数执行调用存储过程的SQL语句,以下是一个示例代码:
#include <mysql/mysql.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
MYSQL *conn;
MYSQL_RES *res;
MYSQL_ROW row;
const char *server = "localhost";
const char *user = "root";
const char *password = "your_password"; /* set me first */
const char *database = "testdb";
conn = mysql_init(NULL);
// Connect to database
if (!mysql_real_connect(conn, server, user, password, database, 0, NULL, 0)) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s
", mysql_error(conn));
exit(1);
}
// Call the stored procedure
if (mysql_query(conn, "CALL your_stored_procedure()")) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s
", mysql_error(conn));
exit(1);
}
res = mysql_use_result(conn);
// Output the result of the stored procedure
printf("Result of the stored procedure:
");
while ((row = mysql_fetch_row(res)) != NULL)
printf("%s
", row[0]);
// Clean up
mysql_free_result(res);
mysql_close(conn);
return 0;
}在这个例子中,我们首先初始化并连接到MySQL数据库,然后使用mysql_query()函数调用名为your_stored_procedure的存储过程,如果存储过程返回结果集,我们可以使用mysql_use_result()和mysql_fetch_row()来遍历并打印这些结果。
创建表
在C语言中创建表也是通过mysql_query()函数执行相应的SQL语句来实现的,以下是一个创建表的示例代码:
#include <mysql/mysql.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
MYSQL *conn;
const char *server = "localhost";
const char *user = "root";
const char *password = "your_password"; /* set me first */
const char *database = "testdb";
conn = mysql_init(NULL);
// Connect to database
if (!mysql_real_connect(conn, server, user, password, database, 0, NULL, 0)) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s
", mysql_error(conn));
exit(1);
}
// Create a table
if (mysql_query(conn, "CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS TestTable(Id INT PRIMARY KEY, Name VARCHAR(255))")) {
fprintf(stderr, "%s
", mysql_error(conn));
exit(1);
}
printf("Table created successfully
");
// Clean up
mysql_close(conn);
return 0;
}在这个例子中,我们连接到MySQL数据库后,使用mysql_query()函数执行CREATE TABLE SQL语句来创建一个名为TestTable的表,如果表已经存在,则不会重复创建。
FAQs
Q1: 如何在C语言中处理存储过程返回的结果集?
A1: 在C语言中,可以使用mysql_use_result()函数获取结果集,然后使用mysql_fetch_row()或mysql_fetch_array()等函数遍历结果集中的每一行,对于每一行数据,可以根据需要进行处理或输出。
Q2: 如果存储过程或创建表的SQL语句执行失败,应该如何处理?
A2: 如果mysql_query()函数返回非零值,表示SQL语句执行失败,此时应该使用mysql_error()函数获取错误信息,并根据错误信息进行相应的错误处理,例如打印错误信息、记录日志或者尝试恢复操作等。
小编有话说
在C语言中调用存储过程和创建表是与数据库交互的常见需求,通过使用MySQL C API提供的函数,我们可以方便地实现这些功能,在实际应用中,还需要注意错误处理、资源管理和安全性等方面的问题,以确保程序的稳定运行和数据的安全。
本站发布或转载的文章及图片均来自网络,其原创性以及文中表达的观点和判断不代表本站,有问题联系侵删!
本文链接:https://www.xixizhuji.com/fuzhu/401985.html