如何通过JDBC成功连接MySQL数据库进行测试?
- 行业动态
- 2024-12-28
- 3250
通过JDBC连接MySQL数据库的步骤包括:加载MySQL JDBC驱动程序,建立连接字符串,创建Connection对象,执行SQL操作。
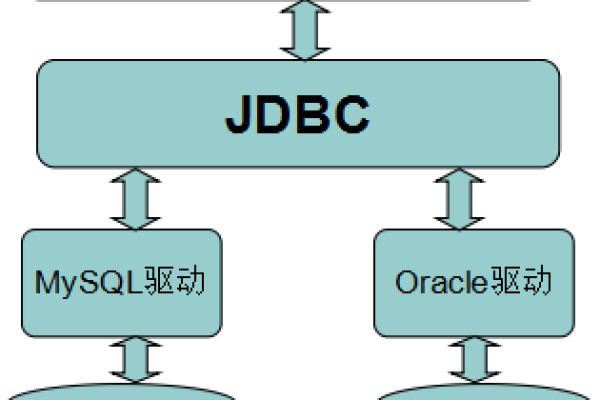
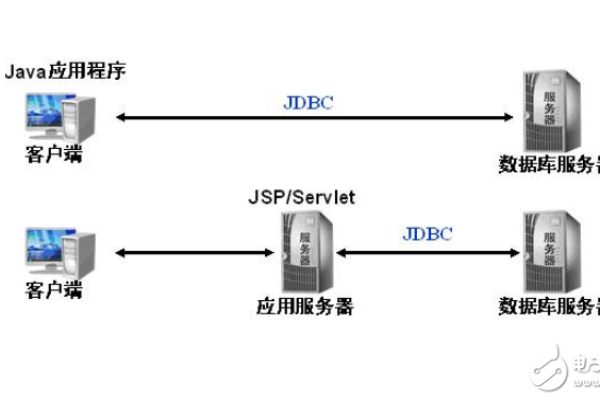
如何通过JDBC连接MySQL数据库

一、准备工作
1. 下载并添加MySQL驱动
需要下载MySQL的JDBC驱动包(Connector/J),该驱动程序是一个JAR文件,可以从MySQL官方网站或Maven仓库获取。
下载地址:https://dev.mysql.com/downloads/connector/j/
下载完成后,将JAR文件添加到项目的类路径中,在Eclipse中可以通过以下步骤完成:
右键点击项目名称,选择Build Path -> Configure Build Path...。
进入Java Build Path,选择Libraries选项卡。
点击Add External JARs...,找到并选择你下载的MySQL驱动JAR文件。
点击Apply and Close。
2. 配置MySQL数据库
确保你的MySQL数据库正在运行,并且你知道以下信息:
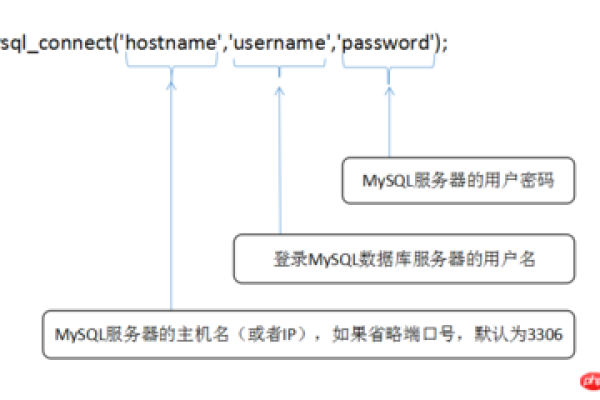
数据库URL:格式为jdbc:mysql://<host>:<port>/<database_name>,例如jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
用户名和密码:用于连接数据库的凭据
二、编写代码连接MySQL数据库
1. 加载驱动类
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}注意:对于较新版本的MySQL驱动,建议使用com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver而不是com.mysql.jdbc.Driver。
2. 创建连接
String dbURL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test";
String userName = "root";
String userPwd = "521123456";
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(dbURL, userName, userPwd);
System.out.println("Connection Successful!");
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (conn != null) conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}3. 执行SQL语句
以下是一个简单的示例,展示如何创建一个表并插入数据:
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String driverName = "com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver";
String dbURL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test";
String userName = "root";
String userPwd = "521123456";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
// 加载驱动类
Class.forName(driverName);
// 创建连接
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(dbURL, userName, userPwd);
System.out.println("Connection Successful!");
// 创建Statement对象
stmt = conn.createStatement();
// 创建表
String createTableSQL = "CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS users " +
"(id INT PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT, " +
"name VARCHAR(50), " +
"age INT)";
stmt.executeUpdate(createTableSQL);
// 插入数据
String insertSQL = "INSERT INTO users (name, age) VALUES " +
"('Alice', 30), " +
"('Bob', 25), " +
"('Charlie', 28)";
stmt.executeUpdate(insertSQL);
// 查询数据
String querySQL = "SELECT * FROM users";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(querySQL);
// 输出结果
while (rs.next()) {
System.out.println("id: " + rs.getInt("id") + ", name: " + rs.getString("name") + ", age: " + rs.getInt("age"));
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException | SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (rs != null) rs.close();
if (stmt != null) stmt.close();
if (conn != null) conn.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}三、常见问题及解决方案
1. 时区问题
在使用新版MySQL驱动时,可能会遇到时区相关的错误,可以通过在连接URL中指定时区来解决:
String dbURL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?serverTimezone=GMT";
2. 中文乱码问题
为了解决中文乱码问题,可以在连接URL中添加字符编码参数:
String dbURL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8";
四、FAQs
Q1:如何更改数据库URL中的端口号?
A1:只需修改连接字符串中的端口号部分即可,如果默认端口3306被占用,可以使用其他端口如3307:
String dbURL = "jdbc:mysql://localhost:3307/test";
Q2:如何捕获并处理SQLException?
A2:可以使用try-catch块来捕获并处理SQLException。
try {
// 可能抛出SQLException的代码
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace(); // 打印异常堆栈跟踪信息
}还可以根据具体的异常类型进行更详细的处理。
五、小编有话说
通过上述步骤,你已经学会了如何使用JDBC连接MySQL数据库,并进行基本的数据库操作,希望这篇指南对你有所帮助!如果你有任何疑问或需要进一步的帮助,请随时留言讨论,祝你编程愉快!
本站发布或转载的文章及图片均来自网络,其原创性以及文中表达的观点和判断不代表本站,有问题联系侵删!
本文链接:http://www.xixizhuji.com/fuzhu/377303.html