网站空间租赁费一年多少钱
- 行业动态
- 2024-04-10
- 1
网站空间租赁费是指为了在互联网上发布和运行网站,个人或企业需要向提供网站托管服务的公司支付的费用,这些费用通常根据提供的服务种类、服务器资源、带宽、存储空间以及其他增值服务不同而有所差异,以下是关于网站空间租赁费的详细说明,包含小标题和单元表格以方便理解:
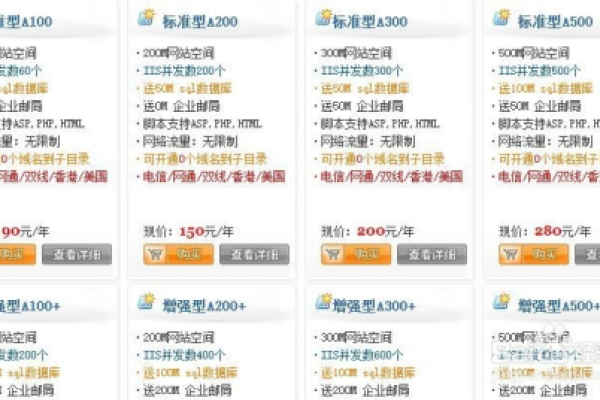
1. 网站空间租赁基础费用
a. 虚拟主机(共享主机)
描述:多个网站共享同一台服务器的资源。
优点:成本较低,适合小型网站或博客。
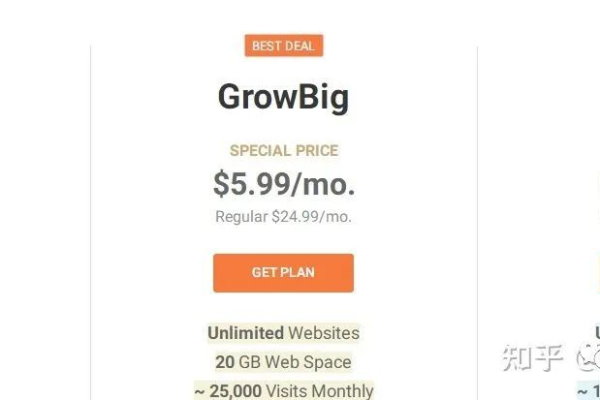
价格范围:每月约 $2 $15 美元不等。
b. VPS主机(虚拟私人服务器)
描述:服务器资源被划分为多个“虚拟”私有服务器。
优点:比共享主机更稳定,提供更多控制。
价格范围:每月约 $20 $100 美元不等。
c. 专用服务器
描述:一台物理服务器仅供一个用户使用。
优点:最高级别的性能和安全性。
价格范围:每月约 $100 $300 美元不等。
d. 云主机
描述:通过云技术分配和扩展资源。
优点:可扩展性强,按需付费。
价格范围:按使用量计费,价格变动较大。
2. 额外服务费用
a. 带宽费用
描述:数据传输量的费用。
计算方式:通常按照GB(千兆字节)计算。
价格范围:超出包含在基础套餐的部分可能需要额外支付。
b. SSL证书
描述:保障网站数据传输安全的标准安全技术。
价格:免费(Let’s Encrypt等)或每年约 $50 $500 美元不等。
c. 备份服务
描述:定期备份网站数据以防丢失。
价格范围:每月约 $1 $10 美元不等。
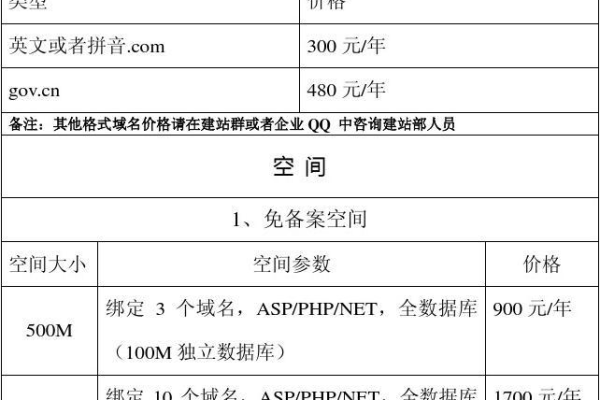
d. 域名注册/转移
描述:网站的网址名称。
价格范围:每年约 $10 $50 美元不等。
e. 技术支持服务
描述:额外的技术支持服务。
价格范围:根据服务提供商和服务等级不同而变化。
3. 附加功能费用
a. 电子商务功能
描述:如购物车系统、支付处理接口等。
价格:根据复杂性和集成程度而定。
b. 内容管理系统(CMS)插件
描述:增强网站功能的插件或模块。
价格:免费至数百美元不等。
c. 自定义设计/开发
描述:个性化的网站设计和编程。
价格:根据项目规模和复杂度,从几百到数千美元不等。
4. 续费和隐藏费用
a. 设置费
描述:初次建立账户时可能产生的一次性费用。
价格:通常是一次性的,约 $0 $100 美元不等。
b. 交易费
描述:在线交易所产生的手续费。
价格:通常为每笔交易金额的百分比。
c. 超流量费用
描述:当网站流量超过既定限额时产生的额外费用。
价格:根据超额的数据量计费。
在选择网站空间租赁服务时,重要的是要了解所有潜在的费用,并考虑任何可能随着业务增长而产生的额外成本,比较不同提供商的套餐和价格,确保选择最适合您当前和未来需求的服务。