如何在Linux系统中创建一个线程?
- 行业动态
- 2024-12-09
- 3
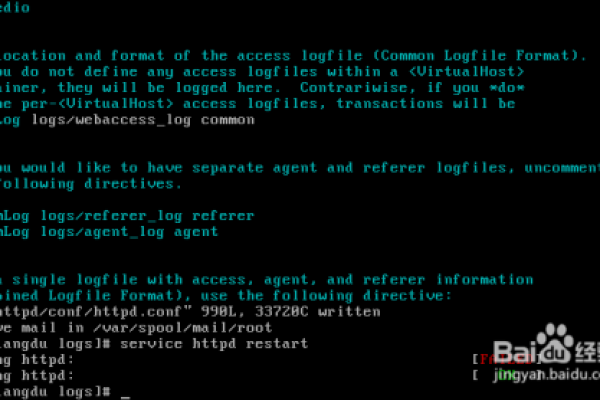
在 Linux 中,可以使用 gcc 编译以下 C 代码来创建一个线程:,,“ c,#include,#include,#include,,void* thread_function(void* arg) {, printf("Hello from the thread!,");, return NULL;,},,int main() {, pthread_t thread;, if (pthread_create(&thread, NULL, thread_function, NULL) != 0) {, fprintf(stderr, "Error creating thread,");, return 1;, }, pthread_join(thread, NULL);, return 0;,},` ,,使用命令 gcc -o create_thread create_thread.c -lpthread` 进行编译。
在Linux操作系统中,线程是程序执行的最小单位之一,与进程相比,线程更加轻量级,因为它们共享同一进程的资源,如内存空间、文件描述符等,创建线程通常使用POSIX线程库(pthread),这是一个广泛使用的C语言库,用于创建和管理线程。
步骤一:包含必要的头文件
要使用pthread库,首先需要包含相应的头文件:
#include <pthread.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h>
步骤二:定义线程函数
线程函数是线程开始执行时调用的函数,这个函数必须接受一个void类型的参数,并返回一个void类型的值。
void* thread_function(void* arg) {
printf("Hello from the thread!
");
return NULL;
}步骤三:创建线程
使用pthread_create函数创建一个新线程,这个函数接受四个参数:
1、指向线程标识符的指针。
2、要执行的线程函数。
3、传递给线程函数的参数。
4、线程属性对象的地址(通常为NULL,表示默认属性)。
pthread_t thread_id;
int result = pthread_create(&thread_id, NULL, thread_function, NULL);
if (result != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error creating thread
");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}步骤四:等待线程结束
使用pthread_join函数等待线程结束,这个函数接受两个参数:
1、线程标识符。
2、指向线程返回值的指针(通常为NULL)。
void* retval;
pthread_join(thread_id, &retval);
printf("Thread ended with return value: %ld
", (long)retval);完整示例代码
以下是一个完整的示例代码,展示了如何在Linux中使用pthread库创建一个线程:
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void* thread_function(void* arg) {
printf("Hello from the thread!
");
return NULL;
}
int main() {
pthread_t thread_id;
int result = pthread_create(&thread_id, NULL, thread_function, NULL);
if (result != 0) {
fprintf(stderr, "Error creating thread
");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// 等待线程结束
void* retval;
pthread_join(thread_id, &retval);
printf("Thread ended with return value: %ld
", (long)retval);
return 0;
}常见问题解答(FAQs)
Q1: 如何传递参数给线程函数?
A1: 可以通过pthread_create函数的第四个参数传递参数给线程函数,这个参数是一个指向任意类型数据的指针,在线程函数内部,可以通过强制转换将这个指针转换为适当的类型来访问数据。
Q2: 如何同步主线程和子线程之间的执行?
A2: 可以使用pthread_join函数来同步主线程和子线程之间的执行,当主线程调用pthread_join时,它会阻塞直到指定的子线程结束,这样可以确保主线程在子线程结束后再继续执行。
小编有话说
创建和管理线程是并发编程的一个重要方面,通过使用POSIX线程库(pthread),我们可以轻松地在Linux中创建和管理线程,多线程编程也带来了一些挑战,如数据竞争和死锁等问题,在使用多线程时,我们需要仔细设计我们的程序,并使用适当的同步机制来避免这些问题。
本站发布或转载的文章及图片均来自网络,其原创性以及文中表达的观点和判断不代表本站,有问题联系侵删!
本文链接:http://www.xixizhuji.com/fuzhu/365830.html