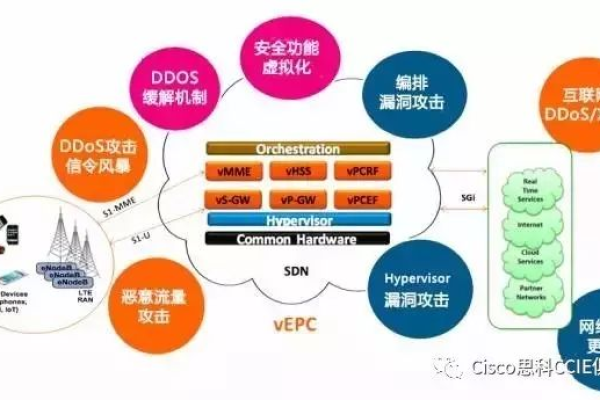
qt如何引用dll
- 行业动态
- 2024-01-18
- 4800
在Qt中引用dll,需要使用 #import指令。确保dll文件与项目文件在同一目录下,然后在头文件中添加 #import指令,指定 dll文件的名称(不包括扩展名)。
在QT中,引用DLL的方法主要有以下几种:
1、使用QLibrary类
QLibrary是Qt提供的一个用于加载和卸载动态链接库(DLL)的类,通过QLibrary类,我们可以方便地实现对DLL的引用和调用。
我们需要创建一个QLibrary对象,并指定要加载的DLL文件名,我们可以使用QLibrary类提供的一些成员函数来获取DLL中的函数地址,并通过这些地址调用DLL中的函数,当不再需要使用DLL时,我们应该调用QLibrary对象的unload()函数来卸载DLL。
以下是一个简单的示例:
include <QLibrary>
include <QDebug>
int main()
{
// 创建一个QLibrary对象,加载名为"mydll.dll"的DLL文件
QLibrary library("mydll.dll");
// 检查DLL是否加载成功
if (library.load()) {
qDebug() << "DLL loaded successfully.";
// 获取DLL中的函数地址
typedef int(*MyFunction)(int, int); // 假设DLL中有一个名为MyFunction的函数,接受两个整数参数,返回一个整数
MyFunction myFunction = (MyFunction)library.resolve("MyFunction");
// 调用DLL中的函数
int result = myFunction(1, 2);
qDebug() << "Result: " << result;
// 卸载DLL
library.unload();
} else {
qDebug() << "Failed to load DLL.";
}
return 0;
}
2、使用Windows API函数LoadLibrary和FreeLibrary
除了使用QLibrary类之外,我们还可以直接使用Windows API提供的LoadLibrary和FreeLibrary函数来加载和卸载DLL,这种方法与使用QLibrary类似,但需要手动处理函数指针和参数类型转换。
以下是一个简单的示例:
include <windows.h>
include <iostream>
include <typeinfo>
include <QDebug>
int main()
{
// 加载名为"mydll.dll"的DLL文件
HMODULE hModule = LoadLibrary("mydll.dll");
if (hModule == NULL) {
std::cerr << "Failed to load DLL." << std::endl;
return 1;
}
// 获取DLL中的函数地址
typedef int(*MyFunction)(int, int); // 假设DLL中有一个名为MyFunction的函数,接受两个整数参数,返回一个整数
MyFunction myFunction = (MyFunction)GetProcAddress(hModule, "MyFunction");
if (myFunction == NULL) {
std::cerr << "Failed to get function address." << std::endl;
FreeLibrary(hModule);
return 1;
}
// 调用DLL中的函数
int result = myFunction(1, 2);
qDebug() << "Result: " << result;
// 卸载DLL
FreeLibrary(hModule);
return 0;
}
3、使用C++11的std::function和std::bind特性
从C++11开始,标准库提供了一些新的特性,如std::function和std::bind,可以帮助我们更方便地调用DLL中的函数,这些特性可以让我们避免手动处理函数指针和参数类型转换。
以下是一个简单的示例:
include <functional>
include <iostream>
include <typeinfo>
include <QDebug>
include <Windows.h>
include <QLibrary>
int main()
{
// 创建一个QLibrary对象,加载名为"mydll.dll"的DLL文件
QLibrary library("mydll.dll");
if (!library.load()) {
qDebug() << "Failed to load DLL.";
return 1;
}
// 获取DLL中的函数地址(使用std::function和std::bind)
typedef int(*MyFunction)(int, int); // 假设DLL中有一个名为MyFunction的函数,接受两个整数参数,返回一个整数
auto myFunction = std::bind(reinterpret_cast<MyFunction>(GetProcAddress(library.handle(), "MyFunction")), std::placeholders::_1, std::placeholders::_2); // 使用std::bind将函数指针转换为std::function对象,并绑定参数类型和占位符值(_1和_2分别表示第一个和第二个参数)
if (myFunction == nullptr) { // 如果绑定失败,说明无法找到对应的函数或参数类型不匹配,此时应该输出错误信息并退出程序(或者尝试其他方法)
本站发布或转载的文章及图片均来自网络,其原创性以及文中表达的观点和判断不代表本站,有问题联系侵删!
本文链接:http://www.xixizhuji.com/fuzhu/352572.html