负载均衡轮训中的原地址有何区别?
- 行业动态
- 2024-11-26
- 3
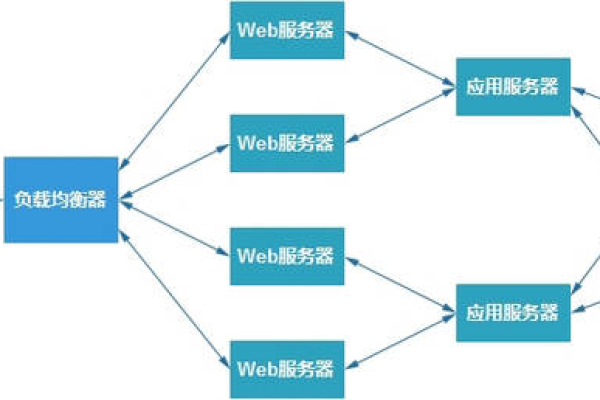
在分布式系统中,负载均衡是确保系统高性能、高并发和高可用性的关键技术之一,轮询算法是其中最简单且应用广泛的负载均衡算法之一,本文将详细介绍三种常见的轮询调度算法:简单轮询、加权轮询和平滑加权轮询,并通过表格和示例代码进行说明。
一、简单轮询
1. 算法描述
简单轮询算法通过依次分配请求到每台服务器上,当所有服务器都被调度一次后,重新开始循环,假设有N台实例S={S1, S2, …, Sn},指示变量currentPos表示当前选择的实例ID,初始化为-1,算法步骤如下:
1、调度到下一个实例;
2、若所有实例已被调度过一次,则从头开始调度;
3、每次调度重复步骤1和2。
2. 示例
以下是一个简单轮询的示例:
| 请求 | currentPos | 选中的实例 |
| 1 | 0 | 192.168.10.1:2202 |
| 2 | 1 | 192.168.10.2:2202 |
| 3 | 2 | 192.168.10.3:2202 |
| 4 | 3 | 192.168.10.4:2202 |
| 5 | 0 | 192.168.10.1:2202 |
3. PHP代码实现
interface RobinInterface {
public function init(array $services);
public function next();
}
class Robin implements RobinInterface {
private $services = [];
private $total;
private $currentPos = -1;
public function init(array $services) {
$this->services = $services;
$this->total = count($services);
}
public function next() {
$this->currentPos = ($this->currentPos + 1) % $this->total;
return $this->services[$this->currentPos];
}
}
$services = [
'192.168.10.1:2202',
'192.168.10.2:2202',
'192.168.10.3:2202',
'192.168.10.4:2202'
];
$robin = new Robin();
$robin->init($services);
for ($i = 0; $i < 5; $i++) {
echo $robin->next() . "
";
}二、加权轮询
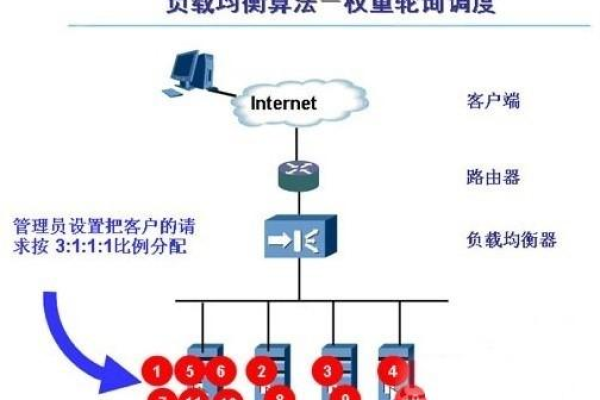
1. 算法描述
加权轮询算法引入了权重的概念,根据每台服务器的性能配置不同的权重,使得高性能服务器能够处理更多的请求,假设有N台实例S={S1, S2, …, Sn},权重W={W1, W2, …, Wn},指示变量currentPos表示当前选择的实例ID,初始化为-1;变量currentWeight表示当前权重,初始值为max(W),算法步骤如下:
1、从上一次调度实例起,遍历后面的每个实例;
2、若所有实例已被遍历过一次,则减小currentWeight为currentWeight-gcd(W),并从头开始遍历;若currentWeight小于等于0,则重置为max(W);
3、直到遍历的实例的权重大于等于currentWeight时结束,此时实例为需调度的实例;
4、每次调度重复步骤1、2、3。
2. 示例
以下是一个加权轮询的示例:
| 服务实例 | 权重值 |
| 192.168.10.1:2202 | 1 |
| 192.168.10.2:2202 | 2 |
| 192.168.10.3:2202 | 3 |
| 192.168.10.4:2202 | 4 |
调度过程如下:
| 请求 | currentPos | currentWeight | 选中的实例 |
| 1 | 3 | 4 | 192.168.10.4:2202 |
| 2 | 2 | 3 | 192.168.10.3:2202 |
| 3 | 3 | 3 | 192.168.10.4:2202 |
| 4 | 1 | 2 | 192.168.10.2:2202 |
| … | … | … | … |
| 9 | 2 | 1 | 192.168.10.3:2202 |
| 10 | 3 | 4 | 192.168.10.4:2202 |
3. JavaScript代码实现
class WeightedRobin {
constructor(services) {
this.services = services;
this.total = services.length;
this.currentIndex = -1;
this.currentWeight = 0;
this.gcd = this.getGcd(services);
}
getGcd(arr) {
return arr.reduce((a, b) => gcd(a, b));
}
gcd(a, b) {
return b === 0 ? a : this.gcd(b, a % b);
}
next() {
while (true) {
this.currentIndex = (this.currentIndex + 1) % this.total;
if (this.currentIndex === 0) {
this.currentWeight -= this.gcd;
if (this.currentWeight <= 0) {
this.currentWeight = Math.max(...this.services.map(item => item[1]));
}
}
if (this.services[this.currentIndex][1] >= this.currentWeight) {
return this.services[this.currentIndex][0];
}
}
}
}
const services = [
{ip: '192.168.10.1', weight: 1},
{ip: '192.168.10.2', weight: 2},
{ip: '192.168.10.3', weight: 3},
{ip: '192.168.10.4', weight: 4}
];
const wrr = new WeightedRobin(services);
for (let i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
console.log(wrr.next());
}三、平滑加权轮询
平滑加权轮询是对加权轮询的改进,通过调整权重的方式避免突发流量导致的负载不均,具体实现较为复杂,通常用于需要更精细控制的场景,以下是其基本思路:
1、记录当前权重:每次调度后记录当前权重。
2、动态调整:根据实时负载动态调整各实例的权重。
3、平滑过渡:逐步调整权重,避免瞬时负载波动。
平滑加权轮询的详细实现涉及更多细节,这里不再展开。
简单轮询适用于服务器性能一致的场景,但无法应对性能差异较大的情况,加权轮询通过引入权重解决了这一问题,使得高性能服务器能够处理更多请求,从而实现更合理的负载分配,平滑加权轮询则进一步优化了加权轮询,适用于需要更精细负载控制的应用场景。
五、FAQs相关问题与解答
Q1: 简单轮询和加权轮询的主要区别是什么?
A1: 简单轮询对所有服务器一视同仁,不考虑服务器性能差异;而加权轮询根据服务器性能分配不同的权重,使得高性能服务器能够处理更多请求。
Q2: 什么时候使用加权轮询而不是简单轮询?
A2: 当服务器性能不一致时,使用加权轮询可以更好地利用高性能服务器的资源,提高整体系统的吞吐量和稳定性。
Q3: 平滑加权轮询与加权轮询有何不同?
A3: 平滑加权轮询在加权轮询的基础上进行了改进,通过动态调整权重和平滑过渡,避免了突发流量导致的负载不均问题,适用于需要更精细负载控制的场景。
以上内容就是解答有关“负载均衡轮训原地址区别”的详细内容了,我相信这篇文章可以为您解决一些疑惑,有任何问题欢迎留言反馈,谢谢阅读。
本站发布或转载的文章及图片均来自网络,其原创性以及文中表达的观点和判断不代表本站,有问题联系侵删!
本文链接:http://www.xixizhuji.com/fuzhu/349000.html