如何解决Win11系统中桌面文件需刷新才能显示的问题?
- 行业动态
- 2024-07-15
- 7
在Windows 11操作系统中,遇到桌面新保存的文件需要手动刷新才能显示的问题,确实可能会给用户带来不便,这种情况通常是由系统设置、缓存问题或是文件管理器的刷新机制导致的,以下是详细的分析:
1、系统设置调整
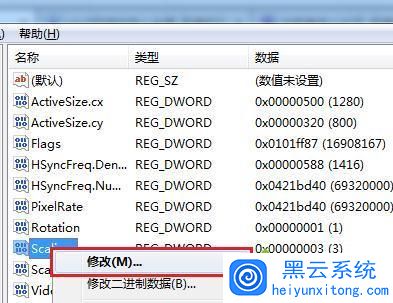
文件夹选项重置:在某些情况下,错误的文件夹选项设置可能导致桌面文件不自动刷新,通过在“文件夹选项”中重置设置,可以解决这一问题,具体步骤包括打开资源管理器,点击“查看”选项卡,然后在“选项”中重置文件夹选项。
隐藏文件和文件夹设置:如果桌面设置了某些文件或文件夹为隐藏属性,那么新文件可能不会立即显示,检查并调整“查看”标签下的“隐藏文件和文件夹”选项,确保其设置不会导致新文件被隐藏。
2、缓存和磁盘空间管理
清理系统缓存:累积的系统缓存有时会影响桌面文件的正常显示,使用磁盘清理工具清理系统缓存,有助于解决新文件不自动刷新的问题。
磁盘空间不足:当系统盘(通常为C盘)空间不足时,也可能导致桌面文件不自动刷新,确保系统盘有足够的空间,可以定期清理不必要的文件和应用,或者使用专业的磁盘管理工具来优化存储空间。

3、文件管理器刷新机制
重置文件管理器:文件管理器可能因为错误配置或损坏导致不能正常刷新,尝试重置文件管理器的设置,恢复到默认状态,有时可以解决问题。
更新系统和应用程序:软件和操作系统的更新通常包含修复已知问题的补丁,确保Windows 11和所有应用程序都更新到最新版本,特别是那些与文件管理相关的应用,如文件资源管理器。
4、系统性能优化
禁用桌面小工具或插件:第三方桌面小工具或插件可能会影响桌面文件的实时显示,尝试禁用这些工具,查看问题是否得到解决。
优化视觉效果和性能设置:在“系统属性”的性能设置中,选择最佳的性能选项,减少视觉特效,有时也能改善桌面文件的显示问题。

5、恢复系统或重置电脑
系统恢复:如果上述方法都不能解决问题,可以考虑使用系统恢复功能,将电脑恢复到出现问题之前的状态。
重置电脑:作为最后的手段,重置Windows 11到初始状态,可以解决由于软件冲突或系统损坏导致的各种问题,包括桌面文件不自动刷新的问题。
在处理这类问题时,建议按照从简到繁的顺序逐步尝试,从最简单的重置文件夹设置开始,逐步过渡到更复杂的系统恢复或重置操作,保持系统的定期更新和合理管理磁盘空间,也是预防此类问题出现的有效方法。
FAQs
Q1: 如果桌面文件仍然不显示,我应该怎么办?

Q2: 如何避免将来出现类似问题?
请按照以上分析和建议的步骤操作,通常情况下可以有效解决Windows 11中桌面文件需手动刷新才能显示的问题。