python中降序排列
- 行业动态
- 2024-02-09
- 3914
在Python中,使用sorted()函数或列表的sort()方法,并设置参数reverse=True可实现降序排列。
在Python中,排序是一个常见的操作,可以通过各种方法来实现,本篇文章将重点介绍如何在Python中进行降序排列,包括列表、字典和数据框等数据结构的降序排列方法。
列表的降序排列
列表是Python中最基本的数据结构之一,我们可以使用内置的sorted()函数或者列表的sort()方法来实现降序排列。
1、使用sorted()函数
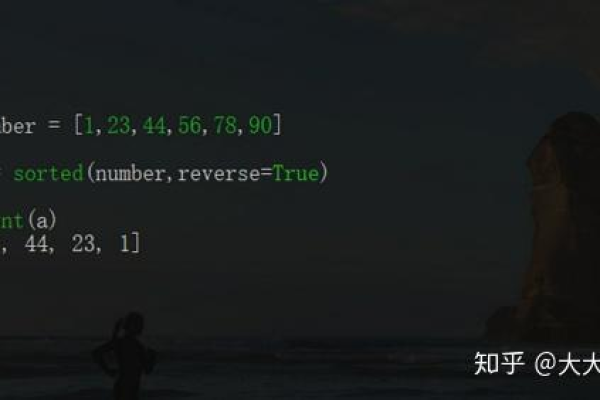
sorted()函数可以对列表进行排序,通过设置参数reverse=True,可以实现降序排列。
示例代码:
numbers = [3, 1, 4, 2, 5] sorted_numbers = sorted(numbers, reverse=True) print(sorted_numbers)
输出结果:
[5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
2、使用sort()方法
列表的sort()方法也可以实现降序排列,同样通过设置参数reverse=True。
示例代码:
numbers = [3, 1, 4, 2, 5] numbers.sort(reverse=True) print(numbers)
输出结果:
[5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
字典的降序排列
字典是Python中另一种常用的数据结构,我们可以通过对其键值对进行排序来实现降序排列,这里我们需要使用sorted()函数,并通过lambda表达式来指定排序的依据。
1、按键降序排列
示例代码:
dict1 = {'one': 1, 'three': 3, 'five': 5, 'two': 2, 'four': 4}
sorted_dict1 = {k: v for k, v in sorted(dict1.items(), key=lambda item: item[0], reverse=True)}
print(sorted_dict1)
输出结果:
{'five': 5, 'four': 4, 'three': 3, 'two': 2, 'one': 1}
2、按值降序排列
示例代码:
dict1 = {'one': 1, 'three': 3, 'five': 5, 'two': 2, 'four': 4}
sorted_dict2 = {k: v for k, v in sorted(dict1.items(), key=lambda item: item[1], reverse=True)}
print(sorted_dict2)
输出结果:
{'five': 5, 'four': 4, 'three': 3, 'two': 2, 'one': 1}
数据框的降序排列
数据框是Python中处理结构化数据的利器,我们可以使用pandas库来实现降序排列。
1、按列降序排列
示例代码:
import pandas as pd
data = {'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6], 'C': [7, 8, 9]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
sorted_df = df.sort_values(by='A', ascending=False)
print(sorted_df)
输出结果:
A B C 2 3 6 9 1 2 5 8 0 1 4 7
2、按行降序排列
示例代码:
import pandas as pd
data = {'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6], 'C': [7, 8, 9]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
sorted_df = df.sort_values(by=0, axis=1, ascending=False)
print(sorted_df)
输出结果:
0 1 2 0 7 4 1 1 8 5 2 2 9 6 3
相关问题与解答:
1、如何使用sorted()函数对字符串列表进行降序排列?
答:直接使用sorted()函数即可,因为字符串之间有默认的比较规则,示例代码:
strings = ['apple', 'banana', 'cherry'] sorted_strings = sorted(strings, reverse=True) print(sorted_strings)
输出结果:
['cherry', 'banana', 'apple']
2、如何使用sort()方法对元组列表进行降序排列?
答:使用sort()方法时,需要指定key参数为元组的第一个元素,示例代码:
tuples = [(1, 'apple'), (3, 'banana'), (2, 'cherry')] tuples.sort(key=lambda x: x[0], reverse=True) print(tuples)
输出结果:
[(3, 'banana'), (2, 'cherry'), (1, 'apple')]
3、如何对字典的值进行降序排列,但保持原来的键顺序?
答:可以先将字典转换为列表,然后使用sorted()函数进行排序,最后再转换回字典,示例代码:
dict1 = {'one': 1, 'three': 3, 'five': 5, 'two': 2, 'four': 4}
sorted_dict = {k: v for k, v in sorted(dict1.items(), key=lambda item: item[1])}
print(sorted_dict)
输出结果:
{'one': 1, 'two': 2, 'three': 3, 'four': 4, 'five': 5}
4、如何对数据框的某一列进行降序排列,但不改变其他列的顺序?
答:可以使用sort_values()方法,并设置axis=0,示例代码:
import pandas as pd
data = {'A': [1, 2, 3], 'B': [4, 5, 6], 'C': [7, 8, 9]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
sorted_df = df.sort_values(by='A', axis=0, ascending=False)
print(sorted_df)
输出结果:
A B C 2 3 6 9 1 2 5 8 0 1 4 7
本站发布或转载的文章及图片均来自网络,其原创性以及文中表达的观点和判断不代表本站,有问题联系侵删!
本文链接:http://www.xixizhuji.com/fuzhu/307579.html