如何在Android应用中实现向服务器发送请求?
- 行业动态
- 2024-11-06
- 8
使用HttpClient或OkHttp等库,通过POST或GET方法,将数据发送至服务器。
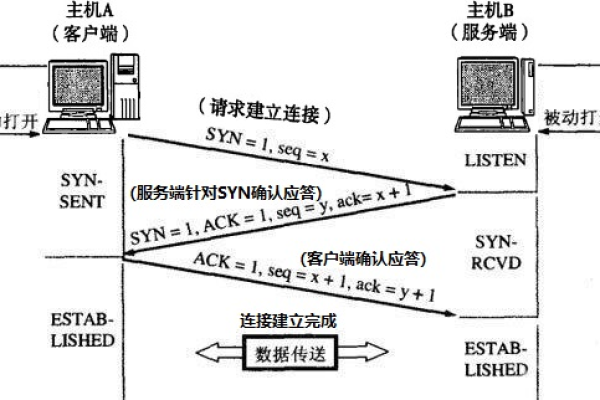
在Android开发中,与服务器进行通信是一项基本且常见的任务,无论是获取数据、提交信息还是执行远程操作,都需要通过HTTP请求来实现,本文将详细介绍如何在Android应用中向服务器发送请求,包括使用HttpURLConnection和OkHttp库两种方式,并探讨如何处理服务器响应。
一、使用HttpURLConnection发送请求
1. 简介
HttpURLConnection是Android SDK提供的一个类,用于建立到指定URL的连接,并发送GET或POST请求,它支持设置超时、读取响应数据等操作。
2. 发送GET请求
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
public class GetRequestExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 创建URL对象
URL url = new URL("http://example.com/api/data");
// 打开连接
HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
// 设置请求方法为GET
connection.setRequestMethod("GET");
// 获取响应码
int responseCode = connection.getResponseCode();
if (responseCode == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK) { // 成功
// 读取响应内容
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(connection.getInputStream()));
String inputLine;
StringBuilder response = new StringBuilder();
while ((inputLine = in.readLine()) != null) {
response.append(inputLine);
}
in.close();
// 打印结果
System.out.println(response.toString());
} else {
System.out.println("GET请求未成功,响应码:" + responseCode);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}3. 发送POST请求
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
public class PostRequestExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
// 创建URL对象
URL url = new URL("http://example.com/api/submit");
// 打开连接
HttpURLConnection connection = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
// 设置请求方法为POST
connection.setRequestMethod("POST");
// 允许写入数据
connection.setDoOutput(true);
// 设置请求头(根据需要)
connection.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", "application/json");
// 准备要发送的数据
String jsonInputString = "{"name": "John", "age": 30}";
// 发送数据
try (OutputStream os = connection.getOutputStream()) {
byte[] input = jsonInputString.getBytes("utf-8");
os.write(input, 0, input.length);
}
// 获取响应码
int responseCode = connection.getResponseCode();
if (responseCode == HttpURLConnection.HTTP_OK) { // 成功
System.out.println("POST请求成功");
} else {
System.out.println("POST请求未成功,响应码:" + responseCode);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}二、使用OkHttp库发送请求
1. 简介

OkHttp是一个高效的HTTP客户端库,相比HttpURLConnection,它提供了更简洁的API和更好的性能,首先需要在项目中添加OkHttp依赖:
implementation 'com.squareup.okhttp3:okhttp:4.9.0'2. 发送GET请求
import okhttp3.OkHttpClient;
import okhttp3.Request;
import okhttp3.Response;
import java.io.IOException;
public class OkHttpGetRequestExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://example.com/api/data")
.build();
try (Response response = client.newCall(request).execute()) {
if (response.isSuccessful() && response.body() != null) {
// 打印结果
System.out.println(response.body().string());
} else {
System.out.println("GET请求未成功,响应码:" + response.code());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}3. 发送POST请求
import okhttp3.*;
import java.io.IOException;
public class OkHttpPostRequestExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OkHttpClient client = new OkHttpClient();
RequestBody body = RequestBody.create(
MediaType.parse("application/json; MediaType.UTF_8), "{"name": "John", "age": 30}");
Request request = new Request.Builder()
.url("http://example.com/api/submit")
.post(body)
.build();
try (Response response = client.newCall(request).execute()) {
if (response.isSuccessful() && response.body() != null) {
// 打印结果
System.out.println(response.body().string());
} else {
System.out.println("POST请求未成功,响应码:" + response.code());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}三、处理服务器响应
无论使用哪种方式发送请求,处理服务器响应都是必不可少的步骤,以下是一些常见的响应处理方式:
| 响应状态码 | 含义 | 处理方式 |
| 200 OK | 请求成功 | 解析响应数据,如JSON、XML等 |
| 400 Bad Request | 客户端错误 | 检查请求参数是否正确 |
| 401 Unauthorized | 未授权 | 检查身份验证信息 |
| 404 Not Found | 资源未找到 | 确认请求的URL是否正确 |
| 500 Internal Server Error | 服务器内部错误 | 联系服务器管理员或稍后重试 |
| 503 Service Unavailable | 服务不可用 | 稍后重试 |
在Android应用中向服务器发送请求是实现网络功能的基础,本文介绍了使用HttpURLConnection和OkHttp库两种常见的方式,并详细讲解了如何发送GET和POST请求以及处理服务器响应,在实际开发中,可以根据项目需求选择合适的方式,并注意处理各种可能的异常情况,以确保应用的稳定性和用户体验。