python3中元组如何表示
- 行业动态
- 2024-04-14
- 4282
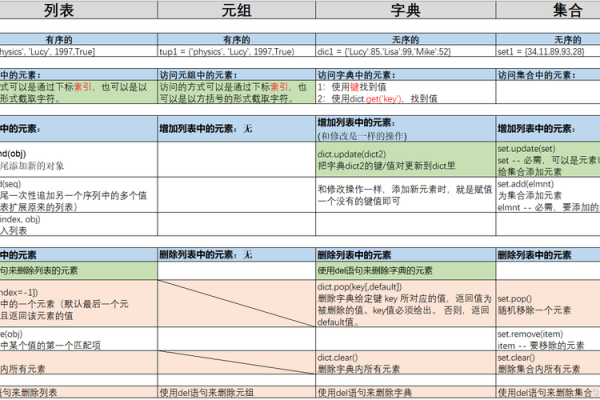
在Python3中,元组是一种不可变的序列类型,用于存储多个元素,元组的元素可以是任何类型的对象,包括数字、字符串、列表等。
1、创建元组:
可以使用圆括号()来创建一个元组,将需要存储的元素放在圆括号内,并用逗号分隔。
“`python
tup = (1, ‘hello’, 3.14)
“`
2、访问元组元素:
可以通过索引来访问元组中的元素,索引从0开始。
“`python
first_element = tup[0] # 结果为1
second_element = tup[1] # 结果为’hello’
“`
3、遍历元组:
可以使用循环语句来遍历元组中的每个元素。
“`python
for element in tup:
print(element)
“`
4、获取元组长度:
使用内置函数len()可以获取元组的长度,即其中元素的个数。
“`python
length = len(tup) # 结果为3
“`
5、切片操作:
可以使用切片操作来获取元组的子集。
“`python
sub_tuple = tup[1:3] # 结果为(‘hello’, 3.14)
“`
6、元组拼接:
可以使用加号+来将两个元组合并成一个新的元组。
“`python
tup1 = (1, ‘hello’)
tup2 = (3.14, True)
concatenated_tuple = tup1 + tup2 # 结果为(1, ‘hello’, 3.14, True)
“`
7、检查元素是否在元组中:
可以使用in关键字来检查某个元素是否在元组中。
“`python
if ‘hello’ in tup:
print("Element exists in the tuple")
“`
8、修改元组:
由于元组是不可变的,所以不能直接修改元组中的元素,但是可以通过创建新的元组来实现元素的修改。
“`python
tup = (1, ‘hello’, 3.14)
new_tuple = (tup[0], ‘world’, tup[2]) # 结果为(1, ‘world’, 3.14)
“`
本站发布或转载的文章及图片均来自网络,其原创性以及文中表达的观点和判断不代表本站,有问题联系侵删!
本文链接:http://www.xixizhuji.com/fuzhu/284157.html