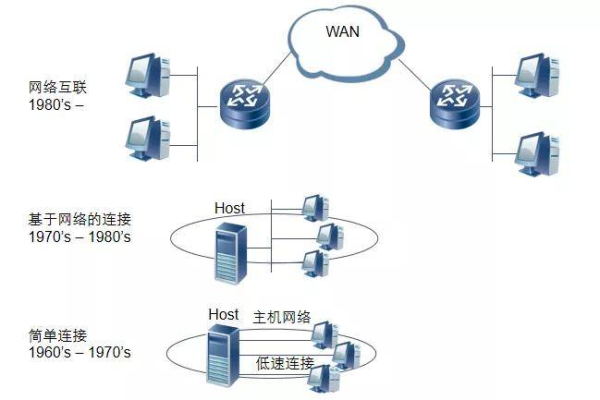
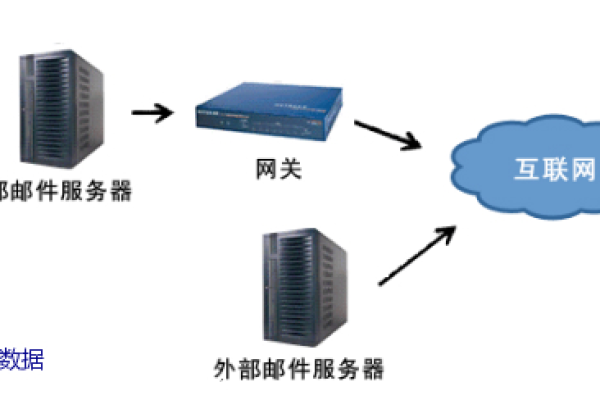
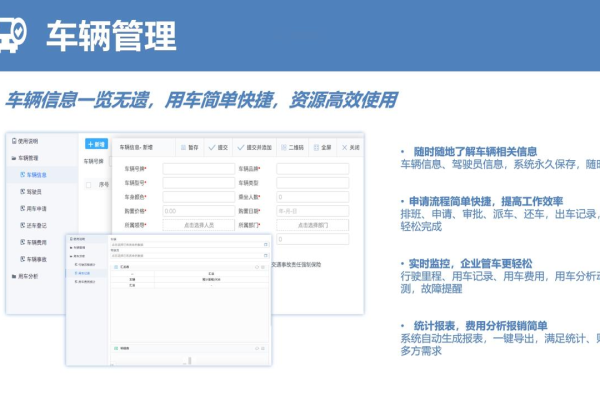
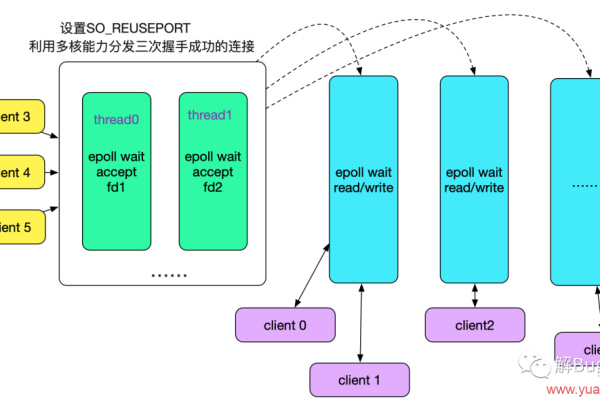
上一篇
c语言获取单个字符
- 行业动态
- 2024-03-21
- 1
在C语言中,字符串是由一系列字符组成的,每个字符都存储在内存中的某个位置,要获取字符串中的单个字符,可以使用索引操作符[],索引操作符的左侧是要访问的字符串,右侧是要访问的字符的索引,索引从0开始,表示字符串中的第一个字符。
以下是一些关于如何在C语言中获取字符串中单个字符的示例:
1、声明和初始化字符串变量
我们需要声明一个字符串变量并为其分配内存,可以使用char数据类型来存储字符,使用malloc函数为字符串分配内存。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
char *str = malloc(10 * sizeof(char)); // 分配10个字符的内存空间
if (str == NULL) {
printf("内存分配失败!
");
return 1;
}
strcpy(str, "Hello, World!"); // 将字符串复制到分配的内存空间
printf("字符串: %s
", str);
// 获取字符串中的单个字符
char ch = str[0]; // 获取第一个字符(索引为0)
printf("第一个字符: %c
", ch);
ch = str[7]; // 获取第八个字符(索引为7)
printf("第八个字符: %c
", ch);
free(str); // 释放内存空间
return 0;
}
2、使用循环遍历字符串中的每个字符
除了使用索引操作符获取字符串中的单个字符外,还可以使用循环遍历字符串中的每个字符,以下是一个使用for循环遍历字符串中的每个字符的示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char *str = malloc(10 * sizeof(char)); // 分配10个字符的内存空间
if (str == NULL) {
printf("内存分配失败!
");
return 1;
}
strcpy(str, "Hello, World!"); // 将字符串复制到分配的内存空间
printf("字符串: %s
", str);
// 使用for循环遍历字符串中的每个字符
for (int i = 0; i < strlen(str); i++) {
char ch = str[i]; // 获取当前字符(索引为i)
printf("%d: %c
", i, ch);
}
free(str); // 释放内存空间
return 0;
}
3、使用指针遍历字符串中的每个字符
另一种遍历字符串中的每个字符的方法是使用指针,以下是一个使用指针遍历字符串中的每个字符的示例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char *str = malloc(10 * sizeof(char)); // 分配10个字符的内存空间
if (str == NULL) {
printf("内存分配失败!
");
return 1;
}
strcpy(str, "Hello, World!"); // 将字符串复制到分配的内存空间
printf("字符串: %s
", str);
// 使用指针遍历字符串中的每个字符
char *p = str; // 将指针指向字符串的第一个字符(地址)
while (*p != ' 本站发布或转载的文章及图片均来自网络,其原创性以及文中表达的观点和判断不代表本站,有问题联系侵删!
本文链接:http://www.xixizhuji.com/fuzhu/258308.html