星讯CDN,它如何优化您的网络体验?
- 行业动态
- 2024-12-09
- 7
星域CDN(星讯CDN)是网心科技推出的一款内容分发网络服务,自2015年6月成立以来,凭借其创新的技术和服务模式,在内容分发网络领域取得了显著的成就,以下是对星域CDN的详细介绍:
一、基本信息
成立时间:2015年6月25日。
公司背景:星域CDN是网心科技倾力打造的新一代互联网内容分发网络,基于迅雷10年的下载与加速技术,并联合小米强大的智能家庭布局能力。
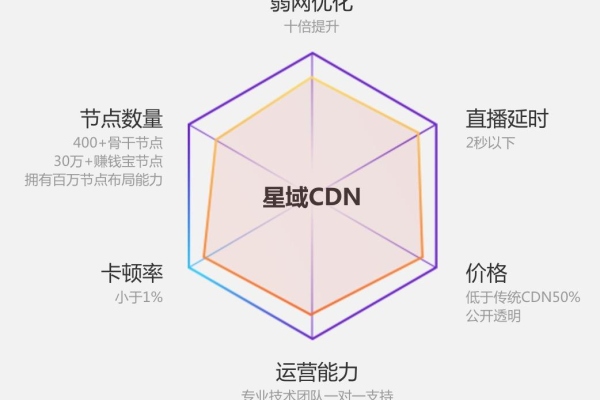
核心优势:拥有国内首创的星域调度技术、弱网加速技术、动态防御技术和无限节点技术,数据传输距离更近、速度更快。
二、技术原理与功能
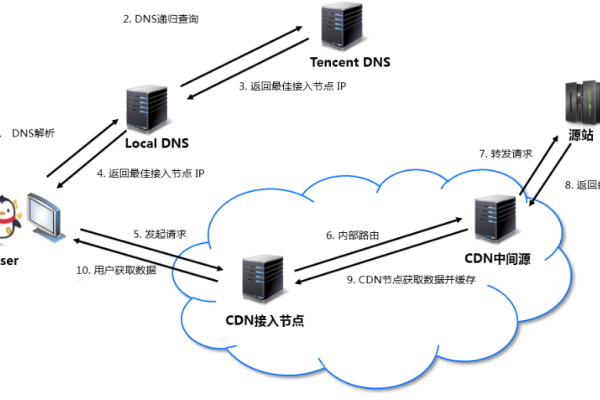
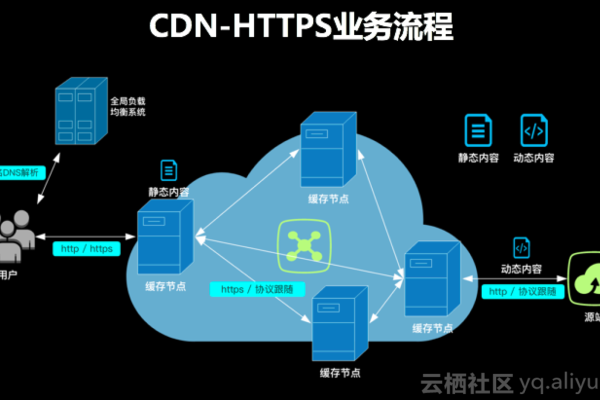
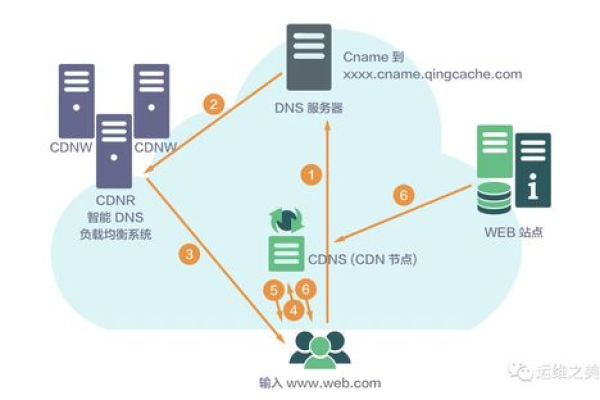
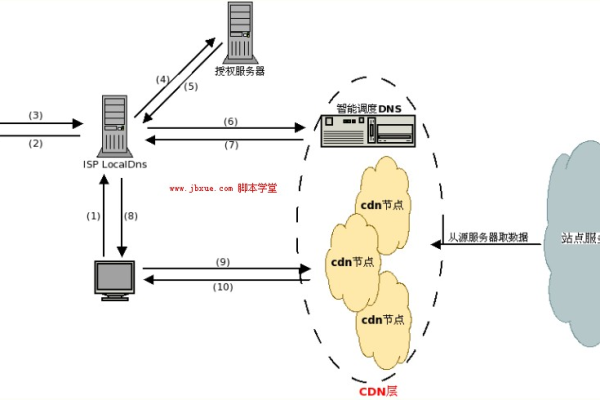
1、内容缓存:将原始内容从源服务器复制并存储到全球分布的多个节点服务器上,当用户请求访问某个内容时,系统会自动从距离用户最近的节点服务器提供内容,从而减少传输延迟,提高访问速度。
2、请求路由:通过分析网络状况、节点负载和用户地理位置等因素,智能地分配用户的请求到最佳的节点服务器。
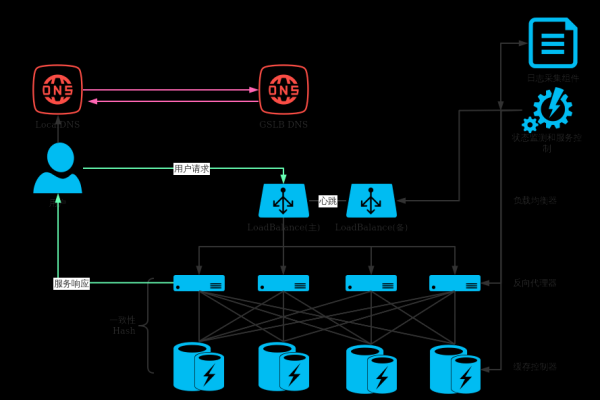
3、负载均衡:确保各个节点服务器的负载均匀分布,从而提高整体系统的稳定性和可靠性。

三、技术创新与优势
1、边缘计算:将计算资源和数据存储部署到靠近用户的边缘节点,提供更低延迟、更高效的内容分发服务。
2、智能调度算法:通过分析网络状况、节点负载和用户地理位置等因素,动态调整内容分发策略。
3、实时监控和分析:对网络状况、节点负载和用户访问情况进行实时监控和分析,及时发现和解决问题。
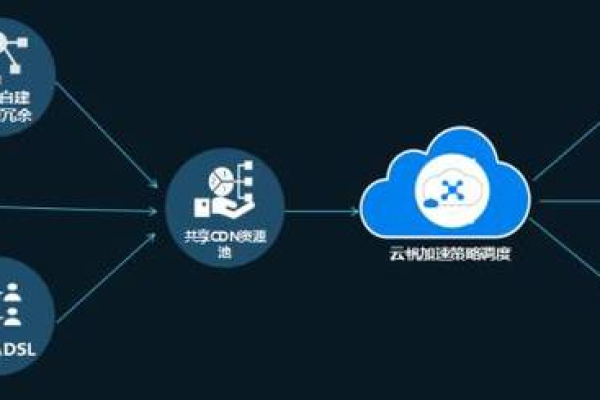
4、无限节点技术:国内首家独创无限节点布局技术,通过拓展数百万级的边缘节点,充分利用无限量的末梢带宽。
5、弱网加速技术:在弱网环境下,通过业内领先的加速技术倍数级提升传输效率与传输质量。
四、应用场景
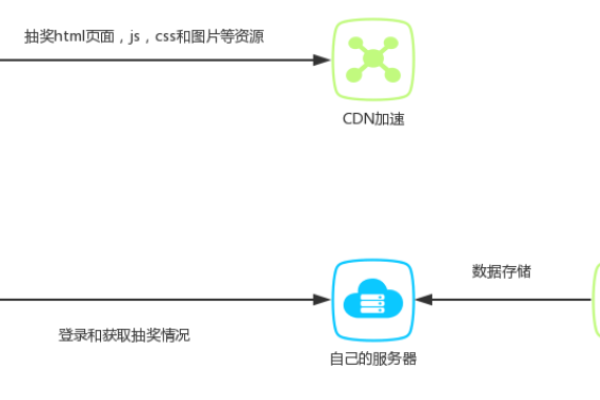
星域CDN在多个领域得到了广泛应用,包括但不限于视频流媒体、在线游戏、电子商务、社交媒体等,在视频流媒体领域,星域CDN能够提供高速、稳定的视频传输服务,保证用户在观看视频时不会出现卡顿、缓冲等问题。
五、市场前景与发展趋势
随着互联网技术的不断发展,星域CDN也在不断进步和创新,随着5G技术的普及和应用,以及人工智能和机器学习技术的进一步发展,星域CDN有望提供更高速、更稳定的内容分发服务,满足用户对高质量内容传输的需求,边缘计算作为星域CDN的重要技术创新,也将在未来得到深入发展。
六、使用流程
使用星域CDN主要包括注册与登录、域名接入、配置加速规则、监控与分析等步骤,用户需要在星域CDN官网上注册账号并登录管理后台;然后将自己的域名接入星域CDN,并进行域名解析设置;接下来配置加速规则,包括缓存策略和安全设置等;最后定期监控和分析CDN的表现,以优化加速策略和提高用户体验。
七、常见问题及解决方案
在使用星域CDN的过程中,可能会遇到一些问题,如域名解析不生效或缓存策略失效等,针对这些问题,用户可以通过检查解析记录设置、刷新缓存配置等方式进行解决。
星域CDN凭借其创新的技术和服务模式,在内容分发网络领域取得了显著成就,随着技术的不断进步和市场的进一步拓展,星域CDN有望为用户提供更加优质、高效的内容分发服务,企业也需要根据自身需求选择合适的CDN服务提供商,并合理配置和使用CDN服务,以实现最佳的加速效果和用户体验。
九、FAQs
Q1: 星域CDN如何帮助提升网站的加载速度和用户体验?
A1: 星域CDN通过将网站内容缓存到全球分布的节点服务器上,使用户能够从距离最近的节点获取内容,从而大幅度减少传输延迟,其智能路由和负载均衡机制保证了用户在访问内容时的稳定性和可靠性,这些措施共同提升了网站的加载速度和用户体验。
Q2: 星域CDN是否支持所有类型的网站和应用场景?
A2: 星域CDN主要适用于需要快速、稳定内容分发的场景,如视频流媒体、在线游戏、电子商务等,对于一些特殊类型的网站或应用(如高度交互式的Web应用、实时性要求极高的在线服务等),可能需要根据具体情况评估CDN的适用性,建议在选择使用前咨询星域CDN的技术支持团队以获取更专业的建议。
十、小编有话说
随着互联网的飞速发展,内容分发网络(CDN)在提升网站性能和用户体验方面发挥着越来越重要的作用,星域CDN作为行业内的佼佼者,以其创新的技术和服务模式赢得了众多企业的青睐,相信在未来的发展中,星域CDN将继续引领行业潮流,为企业提供更加优质、高效的内容分发服务,我们也期待看到更多像星域CDN这样的优秀企业在CDN领域崭露头角,共同推动整个行业的进步和发展。