如何挑选合适的香港虚拟主机配置?
- 行业动态
- 2024-10-19
- 11
香港虚拟主机配置选择要注意什么?以下是一些关键要点:
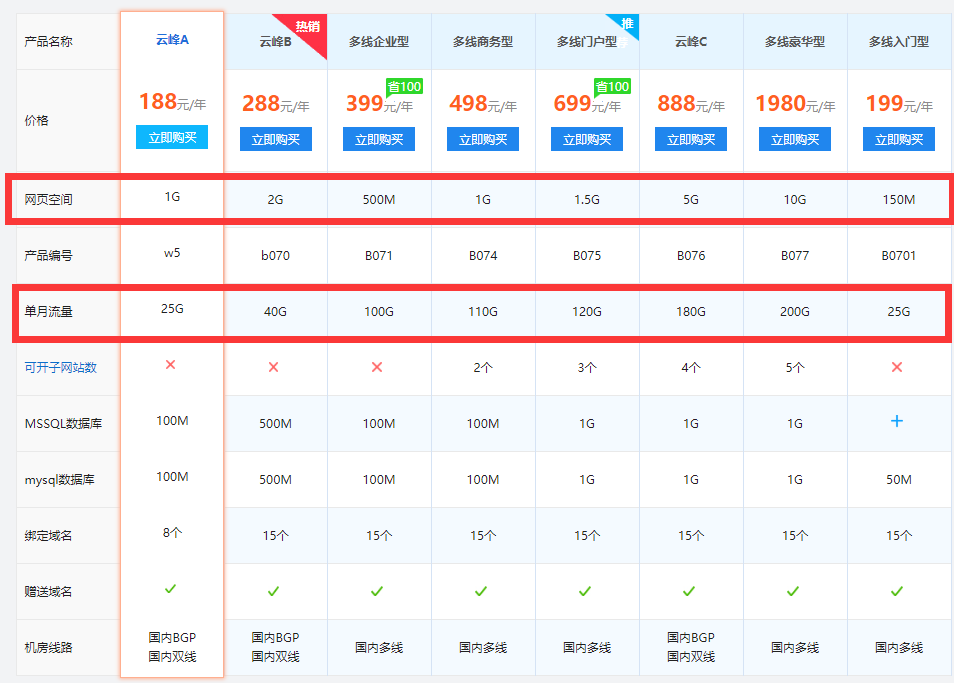
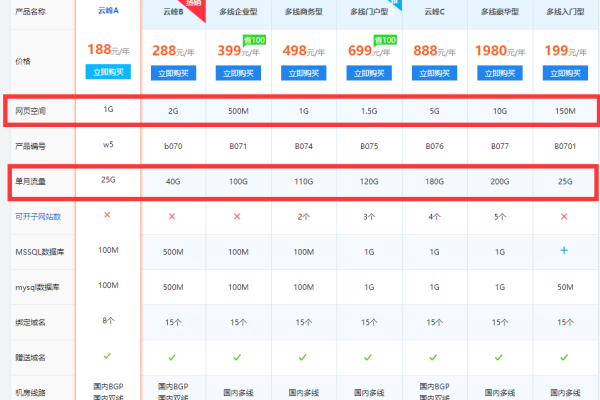
| 方面 | 详细说明 |
| 网站需求分析 | 在选择香港虚拟主机之前,首先要对自身网站进行全面了解,包括建站规模、建站程序、网站性质等,根据网站的具体情况来选择合适的虚拟主机方案,确保其能够满足网站的正常运营需求。 |
| 主机商选择 | 选择有资质、口碑好的主机商非常重要,这可以提供产品质量保障以及优质的售后服务,可以通过对比不同主机商的方案,找到最适合自己的那一个。 |
| 数据中心位置 | 查看托管香港虚拟主机的机房是位于哪个顶级数据机房,因为顶级的数据机房服务器的配置、各项综合性能都比较高,选择位于顶级数据机房的虚拟主机,有助于提高网站的稳定性和访问速度。 |
| 控制面板选择 | 建议选择带有cPanel、Plesk面板的香港虚拟主机,由于这类界面化操作,功能强,简单易懂,所以很容易上手,特别是对于新手站长来说,选择带有这些控制面板的虚拟主机可以大大降低设置和使用的难度。 |
| 性价比考虑 | 虽然香港虚拟主机相比海外虚拟主机价格略高,但要想提升其性价比,可以选择在主机商有促销活动的时候购买,或者寻找相应的优惠码,这样可以在保证虚拟主机质量的同时,降低租用成本。 |
选择香港虚拟主机时需要注意多个方面,通过综合考虑这些因素并做出合理的选择,可以为网站的稳定运行和良好发展奠定坚实的基础。
以上内容就是解答有关“香港虚拟主机配置选择要注意什么”的详细内容了,我相信这篇文章可以为您解决一些疑惑,有任何问题欢迎留言反馈,谢谢阅读。