如何优化电话会议网络系统的服务管理?
- 行业动态
- 2024-07-19
- 6
电话会议网络系统_服务管理
在当今的商业环境中,电话会议网络系统已成为连接远程团队成员、与客户沟通以及进行多方面协作的关键工具,有效的服务管理对于确保这些系统的平稳运行至关重要,本文将探讨电话会议网络系统的服务管理方面,包括系统配置、用户管理、安全性维护和故障排除等关键组成部分。
系统配置
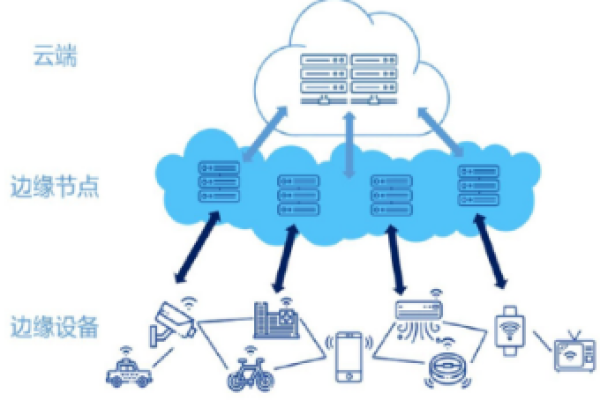
电话会议网络系统的配置是实现高效通信的基础,这通常涉及到硬件的安装、软件的配置以及网络的设置,管理员需要确保所有的设备都正确连接,并且软件更新到最新版本以避免安全破绽,还需要配置适当的带宽和网络协议来支持高质量的音频和视频会议。
用户管理
用户管理是电话会议系统服务管理的另一个重要方面,管理员需要为用户创建账户,分配权限,并监控他们的使用情况,这可能还包括对用户进行培训,以确保他们了解如何有效地使用系统,管理员还需要定期审核用户账户,删除不再使用的账户以保护系统安全。
安全性维护
随着网络攻击的增加,确保电话会议系统的安全性变得尤为重要,服务管理包括实施强密码策略、定期更新软件和固件、监控网络流量以及配置防火墙和加密措施来防止未授权访问,管理员还应制定应急计划,以便在发生安全事件时迅速响应。

故障排除
尽管进行了周密的计划和配置,电话会议系统仍然可能出现技术问题,服务管理包括建立一个有效的故障排除流程,以便快速识别和解决问题,这可能涉及到检查硬件连接、重启系统、审查日志文件以及与技术支持团队合作。
性能监控
为了确保电话会议系统的持续性能,管理员需要监控关键指标,如延迟、丢包率和系统负载,通过定期检查这些指标,可以预见潜在的问题并在它们影响用户体验之前解决它们。
备份与恢复
数据丢失或系统故障可能导致严重的业务中断,服务管理还包括定期备份系统配置和用户数据,并确保可以从备份中快速恢复,这要求有一个清晰的备份计划和恢复流程。
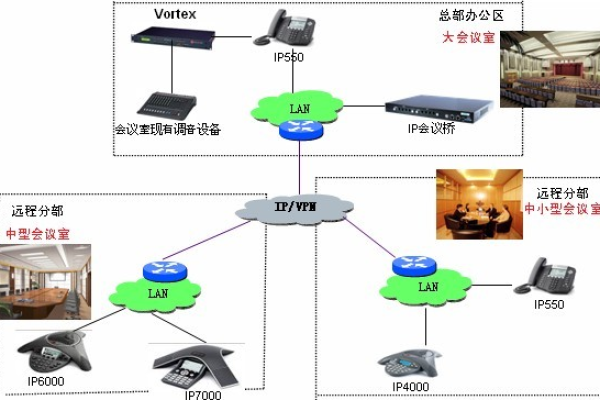
升级与维护
随着时间的推移,软件和硬件都需要升级以保持系统的现代化和安全性,服务管理应包括一个升级计划,该计划详细说明了何时以及如何进行升级,同时最小化对用户的影响。
相关问答FAQs
Q1: 如果我无法加入电话会议,我应该怎么做?
A1: 检查你的网络连接是否稳定,确认你输入的会议ID和密码是否正确,如果问题仍然存在,尝试重新加载会议软件或联系技术支持寻求帮助。
Q2: 我怎样才能确保我的电话会议是安全的?
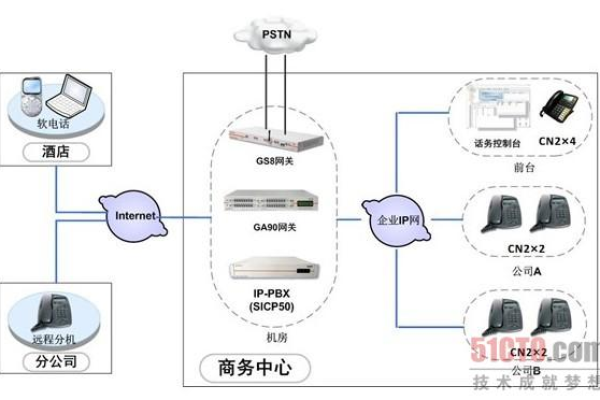
A2: 确保安全性的方法包括使用强密码、定期更新软件、启用加密选项、限制会议访问权限以及监控会议活动,避免在公共网络上举行敏感会议,并确保所有参与者都了解安全准则。
电话会议网络系统的服务管理是一个综合性的过程,它要求管理员不仅要关注技术细节,还要考虑到用户体验和系统安全性,通过遵循上述最佳实践,组织可以确保他们的电话会议系统可靠、高效且安全。