如何通过SEO优化提升电子商务网站的在线可见性和流量?
- 行业动态
- 2024-07-16
- 9
在当今数字化时代,电子商务网站如雨后春笋般涌现,并非所有网站都能获得预期的客流量和销售业绩,搜索引擎优化(SEO)作为提高网站可见性和吸引潜在顾客的关键技术手段,对电子商务网站的成功至关重要,通过精准的SEO设置,网站能够更容易被搜索引擎找到,并在搜索结果中占据较高位置,从而吸引更多点击和访问。
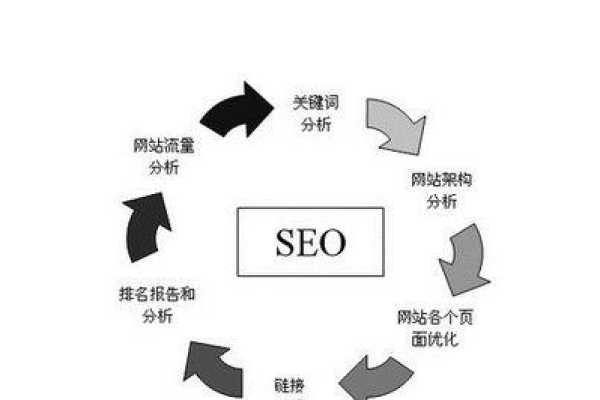
优化的角度考虑,关键词研究是基础,选择与业务相关且用户常用的搜索词汇,并将这些关键词恰当地布置在网站的标题、描述、内容及URL中,提供高质量、独特并且价值大的内容,以及维护清晰、易于导航的页面结构,都是促进用户和搜索引擎喜好的重要做法。
进一步地,网站技术优化也不可忽视,这包括提升网站的加载速度,确保移动设备友好性,以及加强网站的安全性,这些技术层面的优化不仅有利于提升用户体验,而且直接影响搜索引擎对网站的评分和排名。
至于外部链接优化,则需要从获取高质量的外部链接和优化内部链接两个方面着手,高质量的外部链接可以通过合作、投稿和社交媒体等方式获得,而良好的内部链接结构则能有效地分配页面权重,增强网站整体的SEO表现。

除了上述的直接操作之外,利用社交媒体进行网络营销也是提升网站SEO效果的有效途径,通过与用户的积极互动和分享有价值的内容,可以增加网站的曝光度,并进一步引导流量,内容营销策略例如发布博客文章、新闻稿和视频等,同样能够增强网站的可信度和用户参与度。
持续的数据监测与分析对于调整和优化SEO策略来说同样重要,通过分析流量、关键词排名和用户行为数据,企业可以及时调整其SEO策略,以适应搜索引擎算法的更新和市场变化。
电子商务网站要想在激烈的市场竞争中脱颖而出,就必须系统地实施SEO设置,从内容到技术再到外部链接,每一块都需细心打磨并相互支持,社交媒体和内容营销的巧妙运用可进一步提升SEO效果,通过持续监测与分析,企业能够不断优化其策略,以实现最佳的网络推广效果。
相关问答FAQs

Q1: SEO优化中最关键的因素是什么?
A1: SEO优化中最关键的因素包括但不限于:精准的关键词研究与应用、高质量的内容创造、优化的网站结构和技术表现、以及强有力的外部链接建设。
Q2: 如何快速提升电商网站在搜索引擎中的排名?
A2: 快速提升电商网站排名可通过以下方法:(a)针对性的关键词优化;(b)提供独特、高质量的内容并定期更新;(c)改善网站速度和移动端体验;(d)获取高质量的外部链接;(e)持续监测分析竞争对手和搜索引擎算法的变化,并据此调整策略。