c# 修改数据库输出结果
- 行业动态
- 2025-02-22
- 5
csharp,using System;,using System.Data.SqlClient;class Program,{, static void Main(), {, string connectionString = "your_connection_string";, string query = "SELECT * FROM your_table"; using (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString)), {, SqlCommand command = new SqlCommand(query, connection);, connection.Open(); using (SqlDataReader reader = command.ExecuteReader()), {, while (reader.Read()), {, // 修改输出结果, Console.WriteLine($"Column1: {reader["Column1"]}, Column2: {reader["Column2"]}");, }, }, }, },},` 请根据实际需求替换your_connection_string 和your_table`,并调整查询和输出逻辑。
C# 修改数据库输出结果的详细步骤
在C#中,修改数据库中的记录是一个常见的操作,下面将详细介绍如何使用C#代码来修改数据库中的记录,并输出修改后的结果。
准备工作
确保你已经安装了以下工具和库:
.NET SDK
一个支持的数据库(SQL Server、MySQL、SQLite 等)
相应的数据库连接库(例如System.Data.SqlClient 用于 SQL Server,MySql.Data.MySqlClient 用于 MySQL)
创建数据库连接
创建一个数据库连接是进行任何数据库操作的第一步,以下是使用 SQL Server 作为示例的连接字符串:
using System;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
string connectionString = "Server=myServerAddress;Database=myDataBase;User Id=myUsername;Password=myPassword;";
using (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
// 后续代码将在这里编写
}
}
} 请根据你的实际情况替换myServerAddress、myDataBase、myUsername 和myPassword。
打开连接并执行查询
需要打开数据库连接,并执行一个 SQL 查询来修改记录,假设我们要更新一个名为Users 的表中的某个用户的电子邮件地址:
using System;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
string connectionString = "Server=myServerAddress;Database=myDataBase;User Id=myUsername;Password=myPassword;";
using (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
try
{
connection.Open();
string query = "UPDATE Users SET Email = @Email WHERE UserId = @UserId";
using (SqlCommand command = new SqlCommand(query, connection))
{
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Email", "newemail@example.com");
command.Parameters.AddWithValue("@UserId", 1);
int rowsAffected = command.ExecuteNonQuery();
Console.WriteLine($"Rows affected: {rowsAffected}");
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"An error occurred: {ex.Message}");
}
}
}
} 在这个示例中:
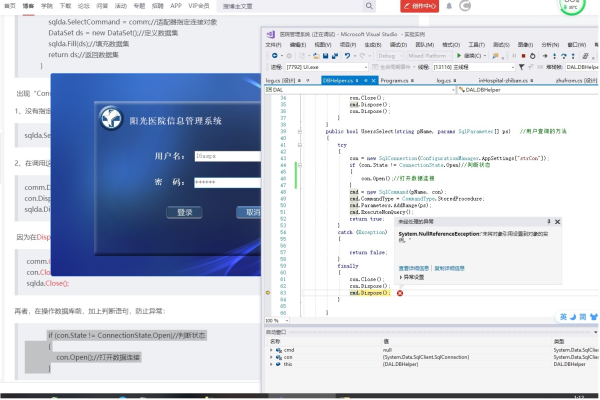
我们使用SqlCommand 对象来执行 SQL 语句。
使用Parameters.AddWithValue 方法来防止 SQL 注入攻击。
ExecuteNonQuery 方法执行更新操作,并返回受影响的行数。
输出结果
在上面的代码中,我们已经输出了受影响的行数,如果需要获取更多信息,可以在更新操作后执行一个SELECT 查询来获取更新后的记录:
using System;
using System.Data.SqlClient;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
string connectionString = "Server=myServerAddress;Database=myDataBase;User Id=myUsername;Password=myPassword;";
using (SqlConnection connection = new SqlConnection(connectionString))
{
try
{
connection.Open();
string updateQuery = "UPDATE Users SET Email = @Email WHERE UserId = @UserId";
using (SqlCommand updateCommand = new SqlCommand(updateQuery, connection))
{
updateCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@Email", "newemail@example.com");
updateCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@UserId", 1);
int rowsAffected = updateCommand.ExecuteNonQuery();
Console.WriteLine($"Rows affected: {rowsAffected}");
}
string selectQuery = "SELECT * FROM Users WHERE UserId = @UserId";
using (SqlCommand selectCommand = new SqlCommand(selectQuery, connection))
{
selectCommand.Parameters.AddWithValue("@UserId", 1);
using (SqlDataReader reader = selectCommand.ExecuteReader())
{
if (reader.Read())
{
Console.WriteLine($"User ID: {reader["UserId"]}, Name: {reader["Name"]}, Email: {reader["Email"]}");
}
}
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"An error occurred: {ex.Message}");
}
}
}
} 在这个扩展的示例中,我们在更新操作后执行了一个SELECT 查询,并使用SqlDataReader 读取结果,然后输出用户的详细信息。
相关问答FAQs
Q1: 如果更新操作没有影响任何行,可能是什么原因?
A1: 可能是以下几个原因:
提供的UserId 不存在于数据库中。
连接字符串或数据库配置有误,导致无法正确连接到数据库。
SQL 语句有语法错误或逻辑错误。
Q2: 如何确保数据库操作的安全性?
A2: 可以采取以下措施来提高数据库操作的安全性:
使用参数化查询以防止 SQL 注入攻击。
确保数据库连接字符串和敏感信息存储在安全的位置,避免硬编码在代码中。
对数据库操作进行适当的异常处理,记录日志以便排查问题。
根据需要对数据进行验证和清理,以防止反面数据的插入或更新。
小编有话说
通过本文的介绍,相信大家已经掌握了在C#中如何修改数据库中的记录,并输出修改后的结果的基本方法,记得在进行数据库操作时,始终要注意安全性和性能优化,以确保应用程序的稳定性和可靠性,如果在实际操作中遇到问题,不妨多查阅官方文档和社区资源,相信一定能找到解决方案。